Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8 : Comprehensive study guide for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 2 “Microorganisms: Friend and Foe”. Includes detailed revision notes covering classification of microbes, friendly uses (food, medicine, agriculture), harmful effects (diseases in humans, animals, plants), food preservation methods, and the nitrogen cycle. Also provides subjective Q&A and MCQs for exam preparation.
Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8:
Table of Contents
📘 SECTION 1: DETAILED REVISION NOTES – Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8
Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8:
1. What are Microorganisms?
Microorganisms or microbes are extremely small living organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye. They can only be seen with the help of a microscope. They are found almost everywhere on Earth—in soil, water, air, inside the bodies of plants and animals, and even in extreme environments like hot springs and polar ice caps.
2. Classification of Microorganisms
Microorganisms are broadly classified into four major groups:
- Bacteria: Single-celled organisms. They have various shapes like rod-shaped (bacilli), spherical (cocci), or spiral.
- Fungi: Plant-like organisms that lack chlorophyll. They can be unicellular (e.g., Yeast) or multicellular (e.g., Bread mould, Penicillium, Aspergillus).
- Protozoa: Single-celled animal-like organisms. (e.g., Amoeba, Paramecium). Some are parasitic and cause diseases like malaria and dysentery.
- Algae: Simple, plant-like organisms that contain chlorophyll and can perform photosynthesis. (e.g., Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas).
- Viruses: Viruses are also microscopic but are different from other microorganisms. They reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism (which could be a bacterium, plant, or animal). Outside a host, they behave like non-living things. They cause diseases like common cold, influenza (flu), polio, and COVID-19.
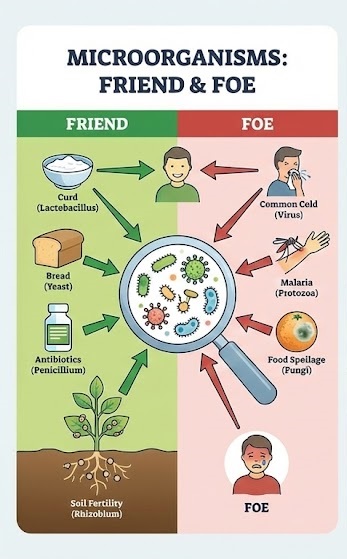
3. Microorganisms: Friendly (Useful)
Microorganisms play an important role in our lives and are used for various purposes:
- A. Making of Curd and Bread:
- Curd: Milk is turned into curd by bacteria. The bacterium Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd. It multiplies in milk and converts it into curd.
- Bread/Cake: Yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of the gas fill the dough and increase its volume. This is the basis for making bread, pastries, and cakes.
- B. Commercial Use:
- Yeast is used for the large-scale production of alcohol, wine, and vinegar (acetic acid).
- Fermentation: The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol by the action of yeast is called fermentation. Louis Pasteur discovered fermentation in 1857.
- C. Medicinal Use:
- Antibiotics: Medicines that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms are called antibiotics. They are produced from bacteria and fungi. (Examples: Penicillin, Streptomycin, Tetracycline).
- Vaccines: When a dead or weakened microbe is introduced into a healthy body, the body fights and kills the invading bacteria by producing antibodies. These antibodies remain in the body and protect us from the disease-causing microbes forever. This is how a vaccine works. Edward Jenner discovered the vaccine for smallpox in 1798.
- D. Increasing Soil Fertility:
- Some bacteria (like Rhizobium living in root nodules of leguminous plants) and blue-green algae are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich the soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility. These are called biological nitrogen fixers.
- E. Cleaning the Environment:
- Microorganisms decompose dead organic waste of plants and animals, converting them into simple substances which are again used by other plants and animals. Thus, they clean up the environment.
4. Microorganisms: Foe (Harmful)
Microorganisms that cause diseases in humans, plants, and animals are called pathogens.
Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8:
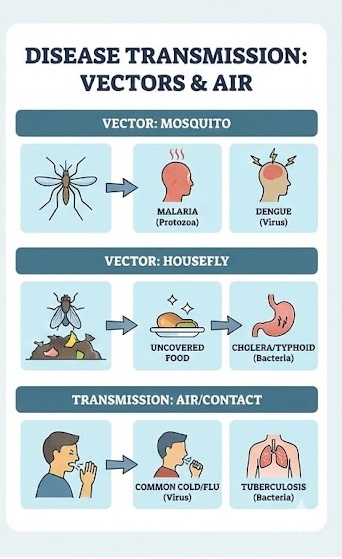
- A. Disease-Causing Microorganisms in Humans:Pathogens enter our body through the air we breathe, the water we drink, or the food we eat. They can also get transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or carried by an animal.
- Communicable Diseases: Diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through air, water, food, or physical contact (e.g., Cholera, Common cold, Chicken pox, Tuberculosis).
- Carriers/Vectors: Some insects and animals act as carriers of disease-causing microbes.
- Housefly: Sits on garbage, pathogens stick to its body, and it transfers them to uncovered food.
- Female Anopheles mosquito: Carrier of the parasite of malaria (Plasmodium).
- Female Aedes mosquito: Carrier of dengue virus.
Common Human Diseases caused by Microorganisms (Important Table):
| Disease | Causative Microorganism | Mode of Transmission |
| Tuberculosis (TB) | Bacteria | Air |
| Measles | Virus | Air |
| Chicken Pox | Virus | Air/Contact |
| Polio | Virus | Air/Water |
| Cholera | Bacteria | Water/Food |
| Typhoid | Bacteria | Water |
| Hepatitis B | Virus | Water |
| Malaria | Protozoa | Mosquito (Vector) |
| Dengue | Virus | Mosquito (Vector) |
- B. Disease in Animals: E.g., Anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium. Foot and mouth disease in cattle is caused by a virus.
- C. Disease in Plants: Microorganisms cause diseases in plants like wheat, rice, potato, etc., reducing crop yield. E.g., Citrus canker (Bacteria), Rust of wheat (Fungi), Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi (Virus).
5. Food Preservation
Microorganisms spoil food. Spoiled food emits a bad smell, has a bad taste, and changes colour. We use methods to prevent this spoilage:
- Chemical Method: Using preservatives like salts and edible oils. Common chemicals used are sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite.
- Preservation by Common Salt: Used to preserve meat, fish, amla, raw mangoes, tamarind. Salt checks the growth of bacteria.
- Preservation by Sugar: Jams, jellies, and squashes are preserved by sugar. Sugar reduces moisture content, inhibiting bacterial growth.
- Preservation by Oil and Vinegar: Used in pickles because bacteria cannot live in such an environment.
- Heat and Cold Treatments: Boiling kills many microorganisms. Low temperature (refrigeration) inhibits the growth of microbes.
- Pasteurization: Milk is heated to about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. This prevents the growth of microbes. Discovered by Louis Pasteur.
- Storage and Packing: Airtight packets prevent the attack of microbes.
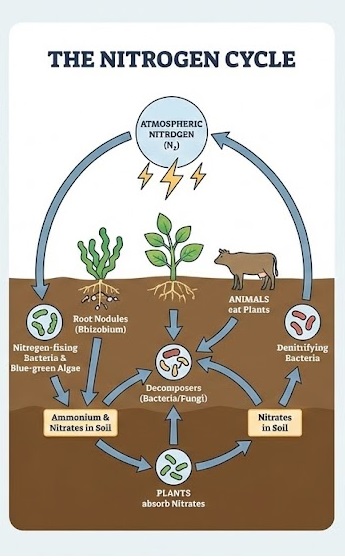
6. Nitrogen Fixation and Nitrogen Cycle
Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8:
- Our atmosphere has 78% nitrogen gas. Plants and animals cannot take nitrogen directly from the atmosphere.
- Nitrogen Fixation: The process of converting atmospheric nitrogen into compounds of nitrogen that plants can use. This is done by Rhizobium bacteria in leguminous plants and also by lightning.
- Nitrogen Cycle: The nitrogen taken from the soil by plants is used to make plant proteins. Animals get these by eating plants. When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi in the soil convert the nitrogenous wastes back into nitrogenous compounds to be used by plants again. Certain other bacteria convert some parts of them to nitrogen gas which goes back into the atmosphere. As a result, the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains nearly constant.
🗣️ SECTION 2: SUBJECTIVE QUESTION AND ANSWERS – Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8
Q1. What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Ans: Antibiotics are medicines produced from bacteria and fungi that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms (e.g., Penicillin).
Precautions:
- Antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor.
- You must finish the course prescribed by the doctor to make the drug completely effective.
- They should not be taken unnecessarily, as it may make the body resistant to the antibiotic when needed in the future.
Q2. Define fermentation. Name the scientist who discovered it.
Ans: The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol by the action of yeast is called fermentation. Carbon dioxide gas is also released during this process. Louis Pasteur discovered fermentation in 1857.
Q3. How does a vaccine work?
Ans: When a dead or weakened disease-causing microbe (vaccine) is introduced into a healthy body, the body fights and kills the invading microbe by producing suitable antibodies. These antibodies remain in the body and remember how to fight the microbe if it enters again. Thus, the body develops immunity against that specific disease.
Q4. Explain how curd is formed from milk.
Ans: Curd contains several microorganisms. Of these, the bacterium Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd. When a small amount of curd (starter) is added to warm milk, the Lactobacillus bacteria multiply in the milk and convert the lactose sugar present in milk into lactic acid, which turns the milk into thick curd.
Q5. What are pathogens? Give two examples of communicable diseases.
Ans: Microorganisms that cause diseases in humans, plants, and animals are called pathogens.
Examples of communicable diseases: Cholera and Common Cold.
Q6. Why is yeast used in the baking industry?
Ans: Yeast is used in the baking industry because it reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide gas during respiration. Bubbles of this gas fill the dough and increase its volume, making bread, pastries, and cakes soft and fluffy.
Q7. What is pasteurization?
Ans: Pasteurization is a method of preserving milk. Milk is heated to about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. This sudden heating and cooling process kills harmful microorganisms present in the milk.
Q8. Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Ans: Rhizobium bacteria (found in roots of leguminous plants) and certain blue-green algae can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
✅ SECTION 3: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) – Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8
1. Which of the following reproduces only inside a host cell?
a) Bacteria
b) Virus
c) Amoeba
d) Fungus
Correct Answer: b) Virus
2. The bacterium responsible for the formation of curd is:
a) Rhizobium
b) Lactobacillus
c) Penicillium
d) Yeast
Correct Answer: b) Lactobacillus
3. Yeast is used in the production of:
a) Sugar
b) Alcohol
c) Hydrochloric acid
d) Oxygen
Correct Answer: b) Alcohol
4. The carrier of the malaria-causing protozoan is:
a) Female Anopheles mosquito
b) Cockroach
c) Housefly
d) Butterfly
Correct Answer: a) Female Anopheles mosquito
5. The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called:
a) Nitrogen fixation
b) Moulding
c) Fermentation
d) Infection
Correct Answer: c) Fermentation
6. Which of the following is an antibiotic?
a) Sodium bicarbonate
b) Streptomycin
c) Alcohol
d) Yeast
Correct Answer: b) Streptomycin
7. Which of the following diseases is caused by a virus?
a) Typhoid
b) Cholera
c) Tuberculosis
d) Polio
Correct Answer: d) Polio
8. Rhizobium bacteria are found in the root nodules of:
a) Cereal plants
b) Leguminous plants
c) All plants
d) Aquatic plants
Correct Answer: b) Leguminous plants
9. Introduction of weakened or dead microbes into the body to develop immunity is called:
a) Sterilization
b) Pasteurization
c) Vaccination
d) Medication
Correct Answer: c) Vaccination
10. Pathogenic micro-organisms present in host cells are killed by medicines called:
a) Painkillers
b) Antibodies
c) Antibiotics
d) Vaccines
Correct Answer: c) Antibiotics
11. Which one of the following is not produced by the process of fermentation?
a) Cheese
b) Milk
c) Yoghurt
d) Wine
Correct Answer: b) Milk
12. Dengue is caused by a virus transmitted by the:
a) Female Anopheles mosquito
b) Female Aedes mosquito
c) Housefly
d) Spider
Correct Answer: b) Female Aedes mosquito
Class 8 Science Chapter 15
Class 8 Science Chapter 13
#Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8
