Crop Production and Management Class 8 : Comprehensive study resource for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 1 “Crop Production and Management”. Includes detailed revision notes covering types of crops (Kharif/Rabi), agricultural practices (Preparation of soil, Sowing, Manure/Fertilizers, Irrigation, Weeding, Harvesting, Storage), and Animal Husbandry. Also provides subjective questions with answers and multiple-choice questions for exam preparation.
Table of Contents
Crop Production and Management Class 8:
📘 SECTION 1: DETAILED REVISION NOTES – Crop Production and Management Class 8
Crop Production and Management Class 8
1. Introduction to Agriculture
- Agriculture: The applied science that deals with the mass production of crop plants and animals useful to human beings is called agriculture.
- Crop: When plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. (e.g., crop of wheat means all plants grown in a field are wheat).
2. Types of Crops in India
Due to diverse climatic conditions, crops in India are broadly classified into two types based on the growing season:
| Feature | Kharif Crops | Rabi Crops |
| Season | Rainy season (Monsoon). | Winter season. |
| Time Period | Sown in June/July, Harvested in Sept/Oct. | Sown in Oct/Nov, Harvested in March/April. |
| Water Requirement | Require lots of water. | Require relatively less water/cold climate. |
| Examples | Paddy (Rice), Maize, Soybean, Groundnut, Cotton. | Wheat, Gram, Pea, Mustard, Linseed. |
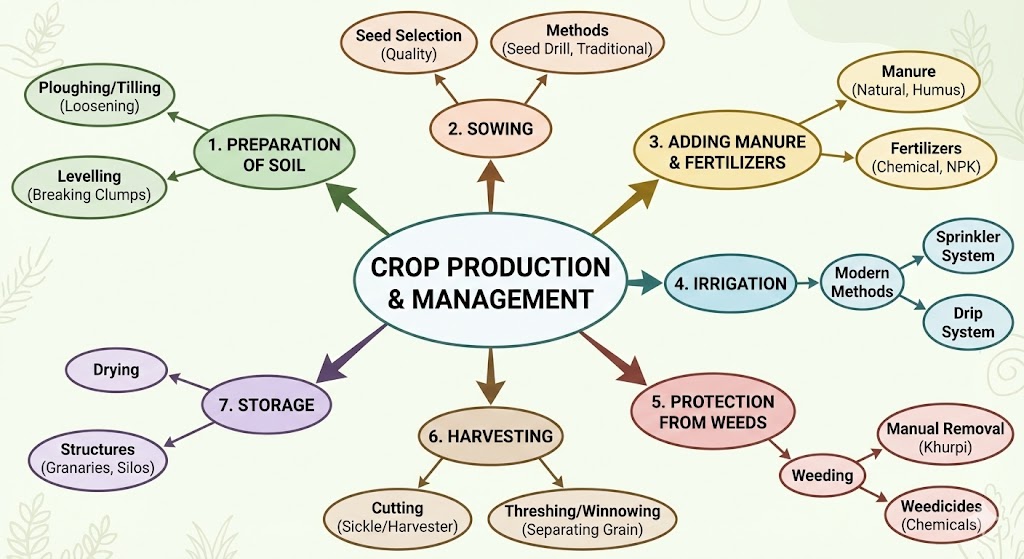
3. Agricultural Practices
Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time. These activities are called agricultural practices. They are:
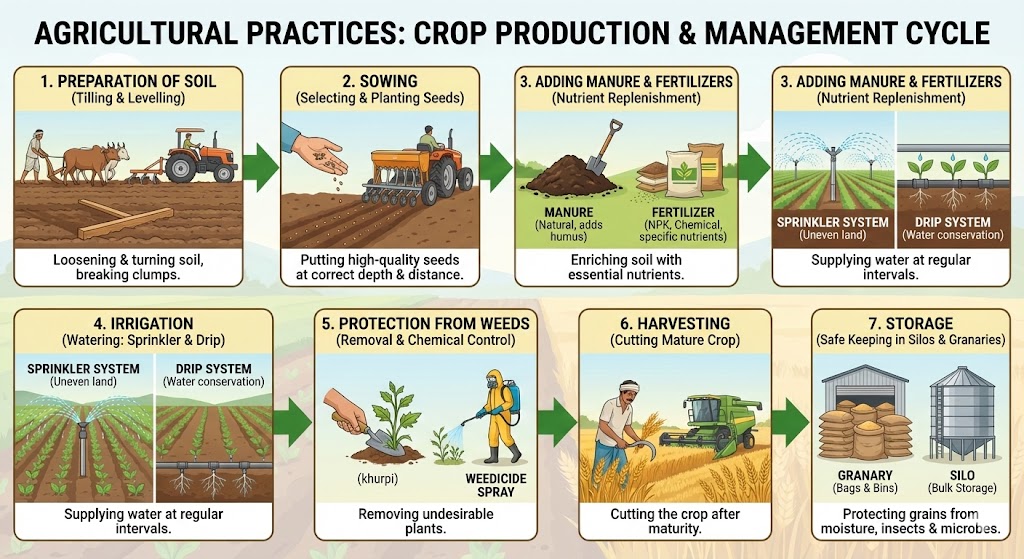
Step 1: Preparation of Soil
- It is the first step before growing a crop.
- Tilling/Ploughing: The process of loosening and turning the soil is called tilling or ploughing.
- Why is it important?
- Allows roots to penetrate deep and breathe easily.
- Helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes (friends of the farmer) which add humus to the soil.
- Brings nutrient-rich soil to the top.
- Tools used: Plough (traditional, wood/iron), Hoe (for removing weeds and loosening soil), Cultivator (tractor-driven, saves labour and time).
- Levelling: Big clumps of soil (crumbs) are broken, and the field is levelled using a leveller for uniform irrigation.
Step 2: Sowing
- The process of putting seeds into the soil.
- Seed Selection: Good quality, clean, and healthy seeds of a high-yielding variety must be selected.
- Methods:
- Traditional Tool: Funnel-shaped tool connected to pipes.
- Seed Drill: Used with a tractor. It sows the seeds uniformly at equal distance and depth. It ensures seeds are covered by soil, preventing damage by birds.
Step 3: Adding Manure and Fertilizers
- Continuous growing of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients. Substances added to the soil to replenish nutrients are called manure and fertilizers.
| Feature | Fertilizer | Manure |
| Nature | Man-made inorganic salt/chemical. | Natural substance obtained by decomposition of cattle dung, plant residues. |
| Preparation | Prepared in factories. | Prepared in the fields. |
| Humus | Does not add humus to the soil. | Provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| Nutrients | Very rich in specific plant nutrients (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium – NPK). | Relatively less rich in specific plant nutrients. |
| Long-term effect | Excessive use pollutes water and soil. | Improves soil texture and water retention capacity. |
- Crop Rotation: Another method of replenishing the soil is growing different crops alternately. (e.g., growing legumes in one season and wheat in the next). Rhizobium bacteria in the root nodules of legumes fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Step 4: Irrigation
- The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation.
- Sources: Wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams, and canals.
- Modern Methods (Efficient water use):
- Sprinkler System: Useful for uneven land or where water is scarce. Rotating nozzles sprinkle water like rain. (Good for coffee, lawns).
- Drip System: Water falls drop by drop directly near the roots. There is zero wastage of water. Best technique for fruit plants, gardens, and areas with acute water shortage.
Step 5: Protection from Weeds
- Weeds: Undesirable plants that grow naturally along with the crop are called weeds (e.g., Amaranthus, grass).
- Weeding: The process of removal of weeds. It is necessary because weeds compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, space, and light, affecting crop growth.
- Methods:
- Manual: Tilling before sowing, or uprooting/cutting them manually with a khurpi.
- Chemical: Using chemicals called weedicides (e.g., 2,4-D). They kill weeds but do not damage the crop.
Step 6: Harvesting
- The cutting of a crop after it is mature is called harvesting.
- Methods: Done manually by a sickle or by a machine called a harvester.
- Threshing: The process of separating grain seeds from the chaff (stalks/husks).
- Winnowing: Separating grain from chaff based on weight using wind (usually done by small farmers).
- Combine: A machine which is both a harvester and a thresher.
Step 7: Storage
- If harvested grains are to be kept for a longer time, they should be safe from moisture, insects, rats, and microorganisms.
- Drying: Grains must be properly dried in the sun to reduce moisture content to prevent attack by microbes (fungi/bacteria).
- Storage structures: Farmers store grains in jute bags or metallic bins. Large scale storage is done in Silos (tall cylindrical structures) and Granaries.
- Home storage: Dried neem leaves are used to keep insects away at home. Chemical treatments are used in large godowns.
4. Animal Husbandry
- Animals reared at home or in farms, provided with proper food, shelter, and care for large-scale production of food (like milk, eggs, meat) is called animal husbandry.
Crop Production and Management Class 8
🗣️ SECTION 2: SUBJECTIVE QUESTION AND ANSWERS – Crop Production and Management Class 8
Crop Production and Management Class 8:
Q1. Differentiate between Kharif and Rabi crops with examples.
Ans:
- Kharif crops are sown in the rainy season (June/July) and harvested in September/October. They require more water. Examples: Paddy, Maize, Soybean.
- Rabi crops are sown in the winter season (October/November) and harvested in March/April. They generally require less water than Kharif crops. Examples: Wheat, Gram, Mustard.
Q2. Why is loosening of soil (ploughing) an important agricultural practice?
Ans: Loosening the soil is important because:
- It allows the roots to penetrate deeper into the soil.
- Loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep.
- It helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes which add humus to the soil.
- It brings nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients.
Q3. What are the advantages of using manure over fertilizers?
Ans: Manure is considered better than fertilizers because:
- It adds humus to the soil and improves soil texture.
- It increases the water-holding capacity of the soil.
- It makes the soil porous, which helps in the exchange of gases.
- It increases the number of friendly microbes.
Q4. Define irrigation. Describe two modern methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Ans: The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation.
Two modern methods that conserve water are:
- Sprinkler System: Perpendicular pipes with rotating nozzles on top are joined to a main pipeline. When water flows under pressure, it escapes from the nozzles and sprinkles on the crop as if it is raining. It is very useful for uneven land and sandy soil.
- Drip System: In this system, water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens, and trees. Water is not wasted at all.
Q5. What are weeds? Why is it necessary to remove them? How can they be controlled?
Ans: Weeds are undesirable plants that grow naturally along with crop plants.
It is necessary to remove them because they compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, space, and light. Thus, they affect the growth of the crop.
They can be controlled by:
- Manual removal: Uprooting or cutting them close to the ground using a khurpi or hoe.
- Tilling: Ploughing the field before sowing helps in uprooting and killing weeds.
- Weedicides: Using chemicals like 2,4-D, which are sprayed in fields to kill the weeds without damaging the crops.
Q6. If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, what would happen?
Ans: Wheat is a Rabi crop, meaning it needs a cool climate and less water to grow. If sown in the Kharif (rainy) season, the crop will not grow properly due to excess water and unfavourable temperature conditions, leading to the destruction of the crop.
✅ SECTION 3: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) – Crop Production and Management Class 8
1. Which of the following is a Rabi crop?
a) Rice
b) Maize
c) Wheat
d) Cotton
Correct Answer: c) Wheat
2. The process of loosening and turning of soil is called:
a) Irrigation
b) Manuring
c) Tilling
d) Sowing
Correct Answer: c) Tilling
3. Which of the following is a traditional method of irrigation?
a) Drip system
b) Sprinkler system
c) Moat (Pulley system)
d) All of these
Correct Answer: c) Moat (Pulley system)
4. 2,4-D is a type of:
a) Fertilizer
b) Manure
c) Weedicide
d) Fungicide
Correct Answer: c) Weedicide
5. The agricultural tool used for sowing seeds with the help of a tractor is called:
a) Plough
b) Seed drill
c) Hoe
d) Cultivator
Correct Answer: b) Seed drill
6. Rhizobium bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and are found in the root nodules of:
a) Cereal plants
b) Leguminous plants
c) Any green plant
d) Aquatic plants
Correct Answer: b) Leguminous plants
7. The process of separating grain from chaff is called:
a) Harvesting
b) Weeding
c) Threshing
d) Sowing
Correct Answer: c) Threshing
8. Which system of irrigation is best suited for areas having acute water shortage?
a) Sprinkler system
b) Drip system
c) Canal irrigation
d) Rahat
Correct Answer: b) Drip system
9. Large scale storage of grains is done in:
a) Jute bags
b) Silos and Granaries
c) Metallic bins
d) Wooden boxes
Correct Answer: b) Silos and Granaries
10. Growing different crops alternately on the same piece of land is called:
a) Crop rotation
b) Intercropping
c) Mixed cropping
d) Weed control
Correct Answer: a) Crop rotation
Class 8 Science Chapter 15
Class 8 Science Chapter 13
#Crop Production and Management Class 8
