Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8 : Complete study guide for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter “Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8” (based on NCERT). Includes concise revision notes covering deforestation, biosphere reserves, national parks, endemic species, and the Red Data Book. Also features subjective Q&A and multiple-choice questions for exam preparation.
Table of Contents
📘 SECTION 1: REVISION NOTES – Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8
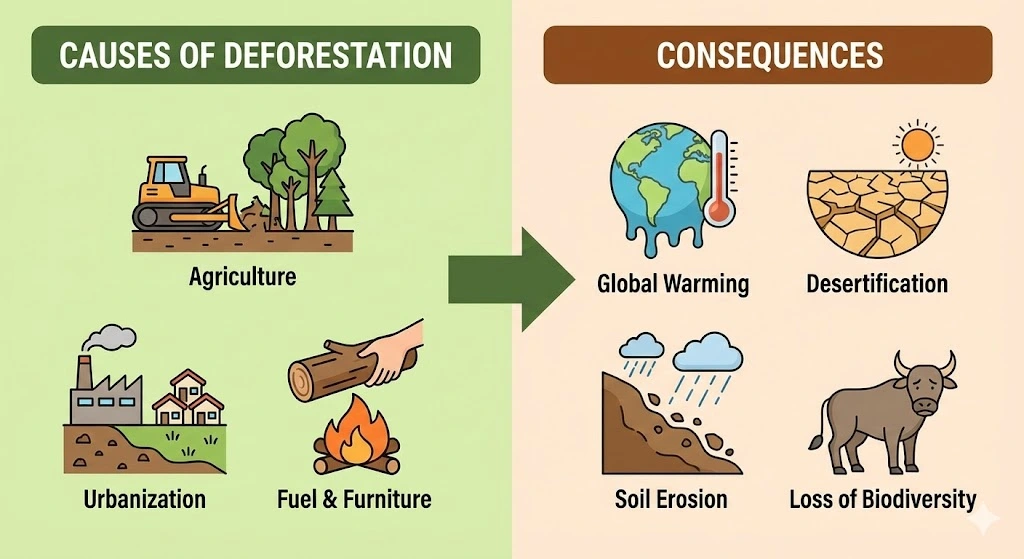
1. Deforestation and its Causes
- Deforestation: The clearing of forests and using that land for other purposes.
- Major Causes:
- Procuring land for cultivation (agriculture).
- Building houses and factories (urbanization).
- Making furniture or using wood as fuel.
- Natural causes like forest fires and severe droughts.
2. Consequences of Deforestation
- Increased Carbon Dioxide: Fewer trees mean less photosynthesis, leading to more CO₂ in the atmosphere, trapping heat and causing global warming.
- Disturbed Water Cycle: Reduced transpiration from trees leads to lower rainfall, causing droughts.
- Soil Erosion: Tree roots hold soil together. Without them, the fertile topsoil is removed by wind and water.
- Desertification: The removal of the top layer of soil exposes the hard, rocky lower layers. Gradually, fertile land converts into deserts.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Destruction of habitats leads to the loss of many plant and animal species.
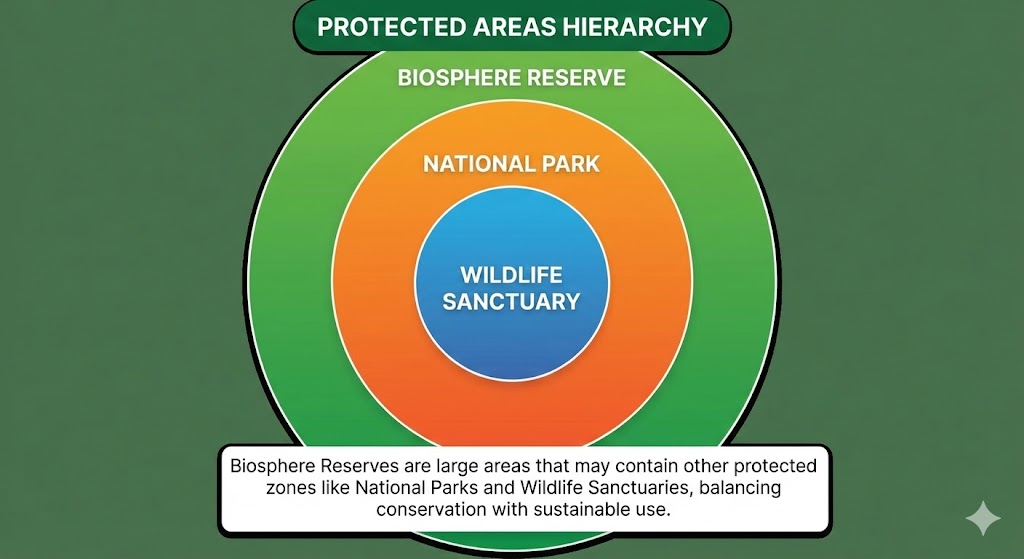
3. Conservation of Forest and Wildlife To protect our flora and fauna and their habitats, the government has established protected areas.
- Biosphere Reserves: Large areas of protected land for the conservation of wildlife, plant, and animal resources, and the traditional life of the tribals living in the area. (Example: Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve).
- Wildlife Sanctuaries: Areas where animals are protected from any disturbance to them and their habitat. Human activities like capturing animals or poaching are strictly prohibited.
- National Parks: Large and diverse reserves able to protect whole sets of ecosystems. They preserve flora, fauna, landscape, and historic objects of an area. (Example: Satpura National Park, the first Reserve Forest of India).
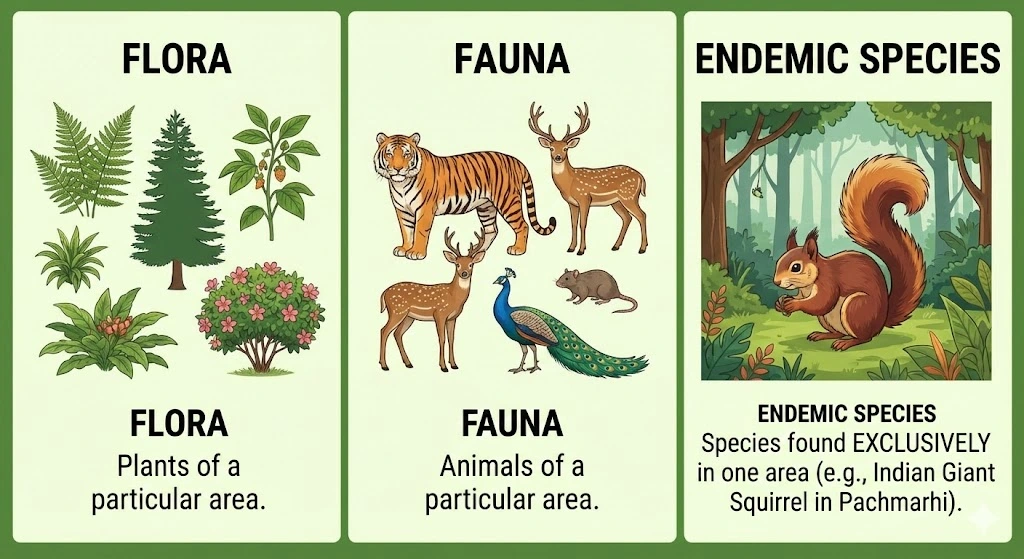
4. Key Biological Terms
- Flora: The plants found in a particular area. (e.g., Sal, teak, mango).
- Fauna: The animals found in a particular area. (e.g., Blue-bull, barking deer, leopard).
- Endemic Species: Species of plants and animals found exclusively in a particular area. They are not naturally found elsewhere. (e.g., Sal and Wild Mango are endemic flora of Pachmarhi; Bison and Indian Giant Squirrel are endemic fauna).
- Species: A group of populations capable of interbreeding.
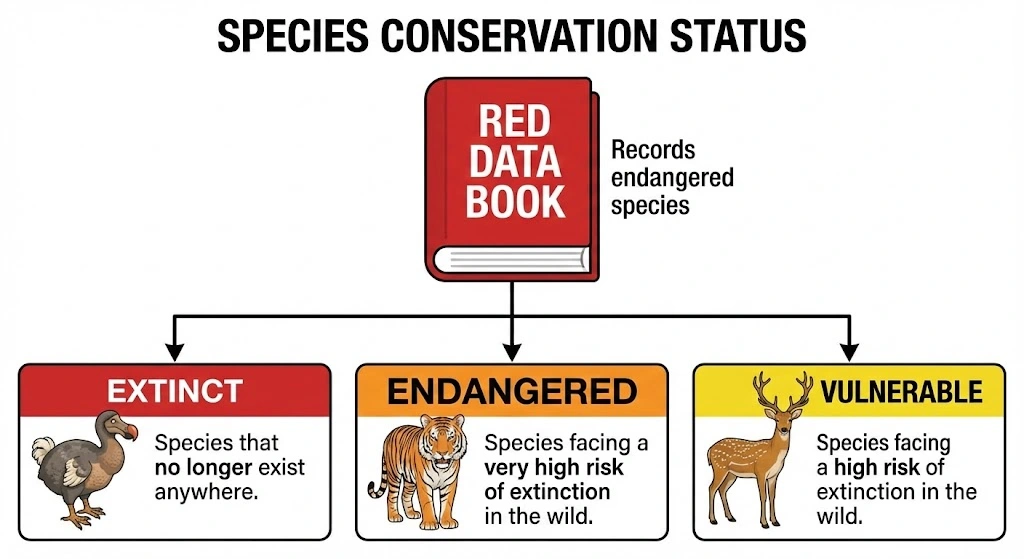
5. Threatened Species and Records
- Endangered Species: Animals whose numbers are diminishing to a level that they might face extinction (e.g., Tiger).
- Extinct Species: Species that no longer exist anywhere on earth (e.g., Dodo).
- Red Data Book: The sourcebook which keeps a record of all the endangered animals and plants. There are different books for plants, animals, and other species.
6. Migration The seasonal movement of animals (usually birds) from their natural habitat to another place for a specific period, usually for breeding or to escape harsh climatic conditions.
7. Practical Steps for Conservation
- Recycling of Paper: It takes 17 full-grown trees to make one tonne of paper. We should save, reuse, and recycle paper to save trees, energy, and water, and reduce harmful chemicals used in papermaking.
- Reforestation: The restocking of destroyed forests by planting new trees. The planted trees should generally be of the same species found in that forest.
🗣️ SECTION 2: SUBJECTIVE QUESTION AND ANSWERS – Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8
Q1: Differentiate between a Wildlife Sanctuary and a Biosphere Reserve. Answer:
- Wildlife Sanctuary: An area reserved specifically for the protection of wild animals. Limited human activities like harvesting timber or collecting minor forest products might be allowed if they don’t disturb the animals.
- Biosphere Reserve: A very large protected area meant for the conservation of biodiversity (plants, animals, and microorganisms) as well as the traditional lifestyle of the tribals living in that vicinity. It may contain other protected areas within it (like national parks and sanctuaries).
Q2: Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall. Answer: Trees absorb groundwater through their roots and release it into the atmosphere as water vapor through the process of transpiration. This water vapor contributes to cloud formation and subsequently rainfall. When forests are cleared (deforestation), the amount of transpiration decreases significantly, leading to fewer clouds and reduced rainfall, which can cause droughts.
Q3: What are endemic species? Why is their conservation very important? Answer: Endemic species are plants or animals that are found exclusively in a specific geographical area and nowhere else naturally. Their conservation is crucial because:
- Their population is usually small and restricted to one place.
- If their specific habitat is destroyed or if a new species is introduced, their entire existence is threatened, leading to quick extinction.
Q4: What is the Red Data Book? Answer: The Red Data Book is the sourcebook published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) that maintains an international record of all endangered plants and animals. It helps in monitoring the status of biodiversity.
Q5: Why are birds like the Siberian Crane known as migratory birds? Answer: Birds like the Siberian Crane fly thousands of kilometers to far-away places during specific times of the year. They migrate because their natural habitats become inhospitably cold and lack food during winter. They travel to warmer regions for survival and breeding, returning when winter ends.
Q6: How does deforestation contribute to global warming? Answer: Plants use carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere for photosynthesis. Deforestation means fewer trees are available to absorb CO₂. This leads to an accumulation of CO₂ in the atmosphere. Since CO₂ is a greenhouse gas that traps heat rays reflected by the earth, its increased concentration leads to an increase in the earth’s average temperature, causing global warming.
✅ SECTION 3: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) – Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8
1. The clearing of forests is referred to as: a) Reforestation b) Afforestation c) Deforestation d) Desertification
Correct Answer: c) Deforestation
2. Which of the following is a result of deforestation? a) Increased rainfall b) Increased soil fertility c) Increased ground water level d) Increased carbon dioxide in the air
Correct Answer: d) Increased carbon dioxide in the air
3. Species found only in a particular area are known as: a) Endangered species b) Endemic species c) Extinct species d) Migratory species
Correct Answer: b) Endemic species
4. The book which keeps a record of endangered species is called: a) Green Data Book b) Blue Data Book c) Red Data Book d) Yellow Data Book
Correct Answer: c) Red Data Book
5. Which of the following is NOT a consequence of deforestation? a) Desertification b) Global warming c) Soil erosion d) Increase in the water table
Correct Answer: d) Increase in the water table (Deforestation actually lowers the water table).
6. A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called a: a) Zoo b) Wildlife Sanctuary c) Aquarium d) Botanical Garden
Correct Answer: b) Wildlife Sanctuary
7. Pachmarhi is an example of a: a) National Park b) Wildlife Sanctuary c) Biosphere Reserve d) Zoo
Correct Answer: c) Biosphere Reserve
8. The process of restocking destroyed forests by planting new trees is called: a) Deforestation b) Reforestation c) Desertification d) Migration
Correct Answer: b) Reforestation
9. The plants found in a particular area are termed as: a) Fauna b) Flora c) Endemic d) Species
Correct Answer: b) Flora
10. Why do birds migrate? a) To see the world b) Due to extreme climatic conditions in their habitat c) Because they run out of water space d) To find other bird species
Correct Answer: b) Due to extreme climatic conditions in their habitat
Class 8 Science Chapter 15
Class 8 Science Chapter 13
#Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8
