Materials Metals and Non-Metals Class 8 Science : Comprehensive study guide for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 4 “Materials: Metals and Non-Metals”. Includes detailed revision notes on physical and chemical properties, displacement reactions, uses, plus subjective Q&A and MCQs for exam preparation.
Table of Contents
📘 SECTION 1: DETAILED REVISION NOTES – Materials Metals and Non-Metals Class 8
1. Introduction to Elements
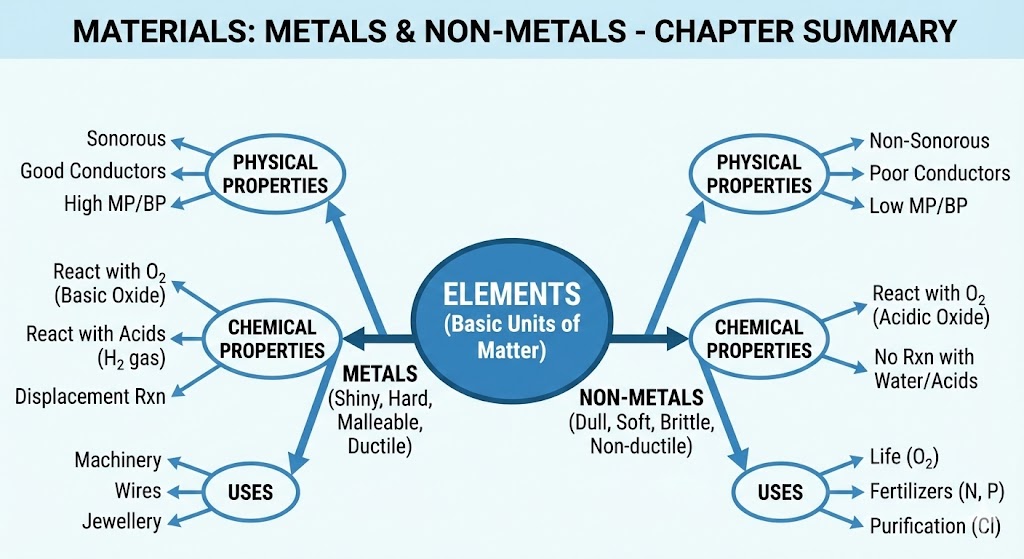
Everything around us is made of matter. The basic unit of matter is an atom. An element is a substance made up of only one kind of atom. There are about 118 known elements. Based on their properties, elements are primarily classified into Metals and Non-Metals.
2. Physical Properties of Metals and Non-Metals
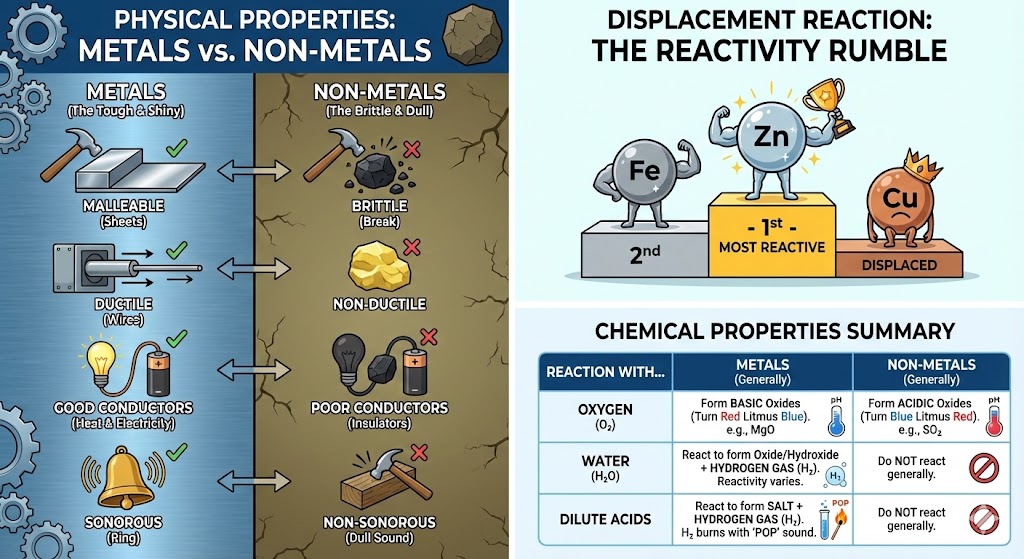
| Property | Metals | Non-Metals | Exceptions/Notes |
| State (at room temp) | Generally Solid. | Solid, Liquid, or Gas. | Mercury is a liquid metal. Bromine is a liquid non-metal. |
| Lustre (Shine) | Lustrous (Shiny). | Dull (No shine). | Iodine and Diamond (Carbon) are lustrous non-metals. |
| Hardness | Generally Hard. | Generally Soft (if solid). | Sodium and Potassium are metals soft enough to be cut with a knife. Diamond is the hardest known natural substance. |
| Malleability (Beaten into sheets) | Malleable. | Brittle (Break upon hammering). | Gold and Silver are highly malleable. |
| Ductility (Drawn into wires) | Ductile. | Non-ductile. | Copper and Aluminum are used for wires. |
| Sonority (Sound on hitting) | Sonorous (Produce ringing sound). | Non-sonorous. | That’s why bells are made of metals. |
| Conduction (Heat & Electricity) | Good Conductors. | Poor Conductors (Insulators). | Graphite (a form of Carbon) is a non-metal but a good conductor of electricity. |
| Melting/Boiling Point | High. | Low. | Gallium and Cesium have very low melting points. |
3. Chemical Properties of Metals
- A. Reaction with Oxygen (Formation of Oxides):
- Metals react with oxygen to form metallic oxides.
- Nature: Metallic oxides are generally basic in nature (turn red litmus blue).
- Example: Burning Magnesium ribbon: $2Mg + O_2 \rightarrow 2MgO$ (Magnesium Oxide). When MgO is dissolved in water, it forms Magnesium Hydroxide $Mg(OH)_2$, which is a base.
- Rusting of Iron: Iron reacts with moist air (oxygen + water vapor) to form rust (hydrated iron oxide).

- B. Reaction with Water:
- Metals react with water to form metal oxides or hydroxides and release hydrogen gas.
- Reactivity varies:
- Sodium/Potassium: React violently with cold water, catching fire. (Stord in kerosene).
- Magnesium: Reacts with hot water.
- Iron/Zinc: React only with steam.
- Copper/Gold/Silver: Do not react with water at all.
- C. Reaction with Acids:
- Most metals react with dilute acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas.
- Test for H₂ gas: It burns with a characteristic ‘pop’ sound when a burning matchstick is brought near it.
- Example: $Zn + 2HCl \rightarrow ZnCl_2 + H_2$
- Exception: Copper does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid even on heating but reacts with sulphuric acid.
- D. Reaction with Bases:
- Some metals (like Aluminium, Zinc) react with strong bases (like NaOH) to produce hydrogen gas.
4. Chemical Properties of Non-Metals
- A. Reaction with Oxygen:
- Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides.
- Nature: Non-metallic oxides are generally acidic in nature (turn blue litmus red).
- Example: Sulphur burns in air: $S + O_2 \rightarrow SO_2$ (Sulphur dioxide). When $SO_2$ dissolves in water, it forms sulphurous acid ($H_2SO_3$).
- B. Reaction with Water:
- Generally, non-metals do not react with water.
- Application: Highly reactive non-metals like Phosphorus catch fire in air, so they are stored in water to prevent contact with atmospheric oxygen.
- C. Reaction with Acids/Bases:
- Generally, non-metals do not react with dilute acids or bases.
5. Displacement Reactions and Reactivity Series
- Reactivity Series: It is an arrangement of metals in decreasing order of their reactivity. (Most reactive at top, least at bottom).
- Simplified Series for Class 8: Potassium(K) > Sodium(Na) > Calcium(Ca) > Magnesium(Mg) > Aluminium(Al) > Zinc(Zn) > Iron(Fe) > Copper(Cu) > Silver(Ag) > Gold(Au).
- Displacement Reaction: A chemical reaction in which a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
- Example: $Fe + CuSO_4 (Blue) \rightarrow FeSO_4 (Green) + Cu$
- Iron is more reactive than copper, so it replaces copper. The blue color fades and turns green.
- Reverse is not possible: Copper cannot displace Iron from Iron sulphate solution because Copper is less reactive than Iron.
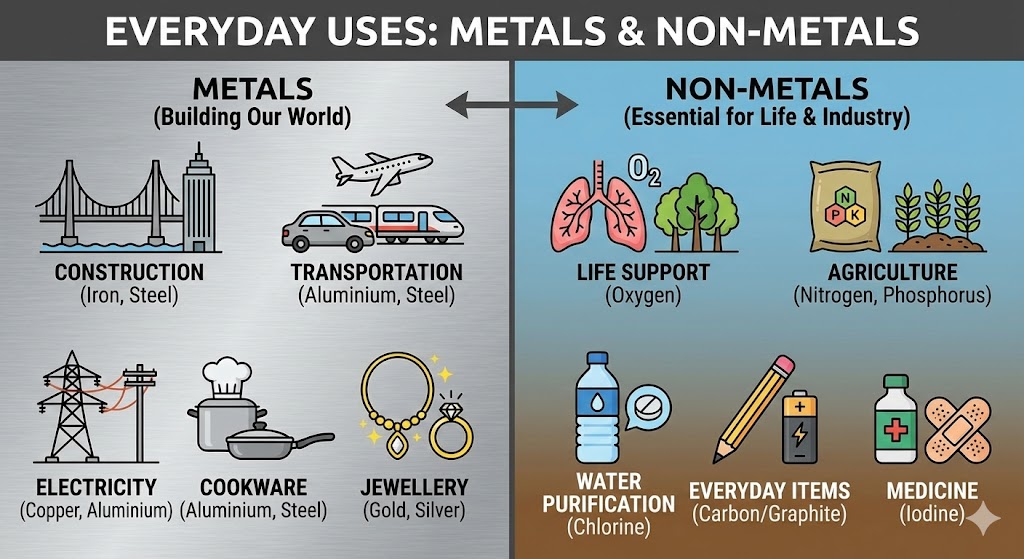
6. Uses of Metals and Non-Metals
- Metals: Machinery, automobiles, aeroplanes, trains, satellites, cooking utensils, water boilers, wires (Cu, Al), jewellery (Au, Ag), packaging (Al foil), thermometers (Mercury).
- Non-Metals: Essential for life (Oxygen for breathing), fertilizers (Nitrogen, Phosphorus), water purification (Chlorine), antiseptic on wounds (Iodine – tincture), crackers (Sulphur, Phosphorus), pencils and batteries (Graphite).
🗣️ SECTION 2: SUBJECTIVE QUESTION AND ANSWERS – Materials Metals and Non-Metals Class 8
Q1. Define malleability and ductility. Ans:
- Malleability: The property of metals by which they can be beaten into thin sheets is called malleability. (e.g., Aluminum foil).
- Ductility: The property of metals by which they can be drawn into thin wires is called ductility. (e.g., Copper wires).
Q2. Why are sodium and potassium stored in kerosene? Ans: Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals. They react vigorously with oxygen and moisture present in the air and even catch fire if kept in the open. To prevent this accidental fire and reaction, they are immersed and stored in kerosene.
Q3. Can you store lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil? Explain. Ans: No, we cannot store lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil. Lemon pickle contains acids (citric acid). Aluminium is a metal, and metals react with acids to produce poisonous salts and hydrogen gas. This reaction can spoil the pickle and make it unfit for consumption.
Q4. What happens when dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate? Ans: Copper is a less reactive metal. It does not react with dilute sulphuric acid, so no visible change occurs. However, it reacts with concentrated or hot sulphuric acid.
Q5. Explain why zinc metal can displace copper from copper sulphate solution, but copper cannot displace zinc from zinc sulphate solution. Ans: Displacement reactions follow the reactivity series. A more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
- Zinc is more reactive than copper. Therefore, when zinc is added to copper sulphate solution, it displaces copper.
- Copper is less reactive than zinc. Therefore, it cannot displace zinc from zinc sulphate solution.
Q6. State three uses of non-metals. Ans:
- Oxygen is essential for respiration by all living beings.
- Chlorine is used for the purification of water to kill germs.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus are used in fertilizers to enhance plant growth.
- (Optional) Iodine is used as an antiseptic solution (tincture of iodine) on wounds.
Q7. Why are electric wires coated with plastic-like materials? Ans: Metals like copper and aluminum are used inside electric wires because they are good conductors of electricity. However, to protect us from electric shocks should we touch the wires, they are coated with materials like plastic or rubber, which are insulators (bad conductors of electricity).
✅ SECTION 3: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) – Materials Metals and Non-Metals Class 8
1. Which of the following is a liquid metal at room temperature? a) Sodium b) Mercury c) Bromine d) Iron
Correct Answer: b) Mercury
2. The property by which metals produce a ringing sound when struck hard is called: a) Malleability b) Ductility c) Sonority d) Lustre
Correct Answer: c) Sonority
3. Which non-metal is essential for our life and inhaled during breathing? a) Nitrogen b) Carbon c) Oxygen d) Hydrogen
Correct Answer: c) Oxygen
4. Metals generally react with acids to produce _____ gas. a) Oxygen b) Nitrogen c) Carbon dioxide d) Hydrogen
Correct Answer: d) Hydrogen
5. Which of the following is the most reactive metal among the options? a) Iron b) Copper c) Sodium d) Zinc
Correct Answer: c) Sodium
6. The best conductor of electricity among the following is: a) Coal b) Sulphur c) Silver d) Wood
Correct Answer: c) Silver
7. Metallic oxides are generally ________ in nature. a) Acidic b) Basic c) Neutral d) Amphoteric
Correct Answer: b) Basic
8. Which non-metal is used in water purification? a) Iodine b) Chlorine c) Sulphur d) Carbon
Correct Answer: b) Chlorine
9. Why is Phosphorus kept in water? a) To keep it cool. b) To prevent it from reacting with atmospheric oxygen. c) To clean it. d) It reacts with water to produce energy.
Correct Answer: b) To prevent it from reacting with atmospheric oxygen.
10. When an iron nail is placed in copper sulphate solution, the color of the solution changes from blue to green due to the formation of: a) Copper oxide b) Iron sulphate c) Copper chloride d) Sulphur dioxide
Correct Answer: b) Iron sulphate
11. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic property of non-metals? a) They are brittle. b) They are poor conductors of heat. c) They are ductile. d) They are dull in appearance.
Correct Answer: c) They are ductile.
12. The ‘pop’ sound indicates the presence of which gas? a) Oxygen b) Carbon dioxide c) Nitrogen dioxide d) Hydrogen
Correct Answer: d) Hydrogen
Class 8 Science Chapter 15
Class 8 Science Chapter 13
#Materials Metals and Non-Metals Class 8
