Coal and Petroleum Class 8: Complete study guide for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 5 “Coal and Petroleum Class 8”. Includes detailed revision notes covering formation and uses of coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Also provides subjective questions with answers and multiple-choice questions for exam preparation.
Table of Contents
📘 SECTION 1: DETAILED REVISION NOTES – Coal and Petroleum Class 8
1. Natural Resources
Anything in the environment which can be used by human beings is called a natural resource. They are broadly classified into two types:
- Inexhaustible Natural Resources: These resources are present in unlimited quantities in nature and are not likely to be exhausted by human activities.
- Examples: Sunlight, air.
- Exhaustible Natural Resources: The amount of these resources in nature is limited. They can be exhausted by continuous human use.
- Examples: Forests, wildlife, minerals, coal, petroleum, natural gas.
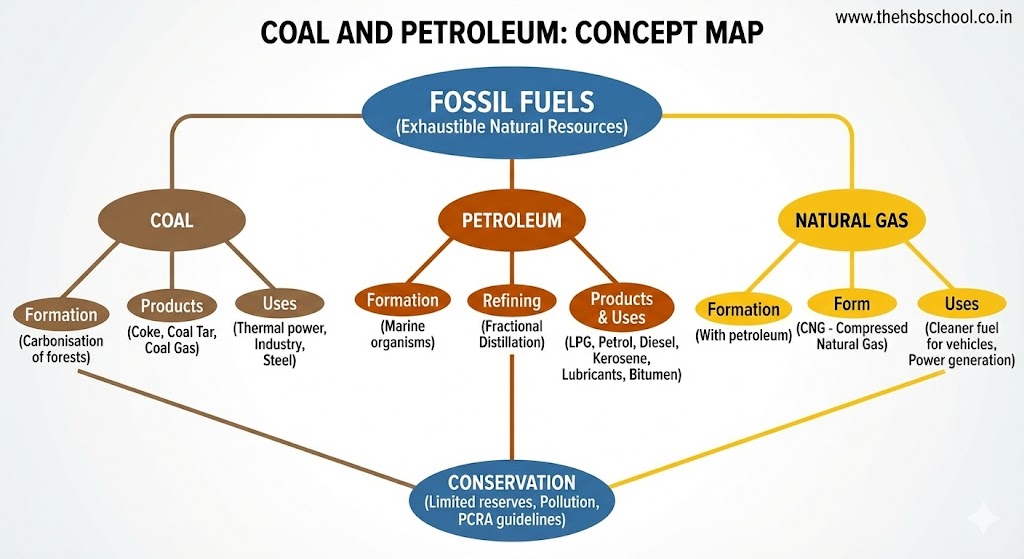
2. Fossil Fuels
Exhaustible natural resources formed from the dead remains of living organisms (fossils) buried under the earth for millions of years are called fossil fuels. Coal, petroleum, and natural gas are fossil fuels.
3. Coal
- Description: Coal is a hard, black-colored fossil fuel, similar to stone.
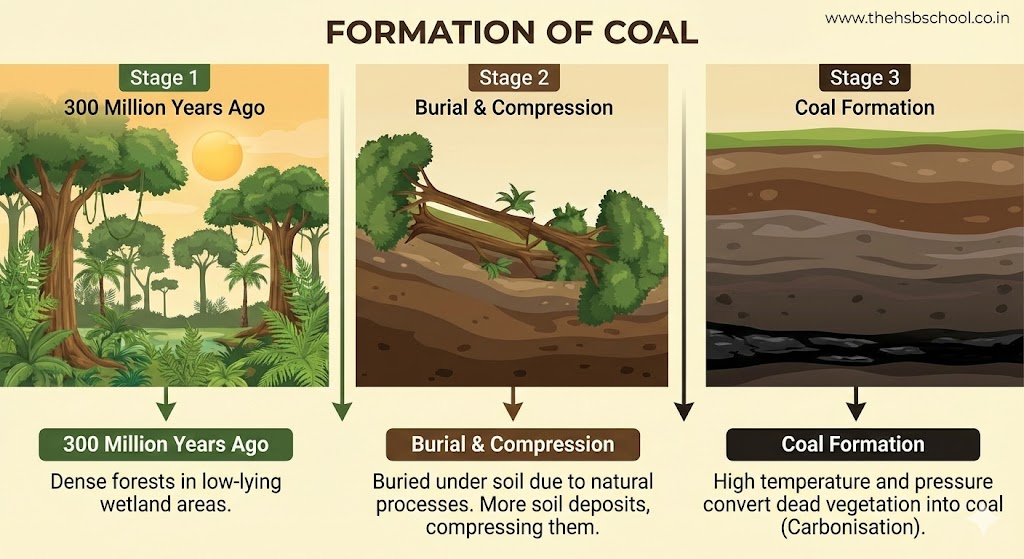
- Formation of Coal:
- Millions of years ago, dense forests existed in low-lying wetland areas on earth.
- Due to natural processes like flooding, these forests got buried under the soil.
- As more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. The temperature also rose as they sank deeper and deeper.
- Under high pressure and high temperature, dead plants were slowly converted to coal.
- Carbonisation: The slow process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called carbonisation. Since coal is mainly formed from plant remains, it is also called a fossil fuel.
4. Products Obtained from Coal
When coal is heated in the absence of air (destructive distillation), useful products are obtained:
- i) Coke: It is a tough, porous, and black substance. It is almost a pure form of carbon.
- Uses: Manufacture of steel and extraction of many metals.
- ii) Coal Tar: It is a black, thick liquid with an unpleasant smell. It is a mixture of about 200 substances.
- Uses: Starting material for manufacturing synthetic dyes, drugs, explosives, perfumes, plastics, paints, and naphthalene balls (used to repel moths).
- Note: These days, Bitumen (a petroleum product) is used for metalling roads instead of coal tar.
- iii) Coal Gas: It is obtained during the processing of coal to get coke.
- Uses: It is used as a fuel in many industries situated near coal processing plants. (Earlier used for street lighting).
5. Petroleum
- Description: Petrol and diesel are obtained from a natural resource called petroleum. It is a dark, oily liquid with an unpleasant odor. It is also called “Black Gold” due to its commercial importance.
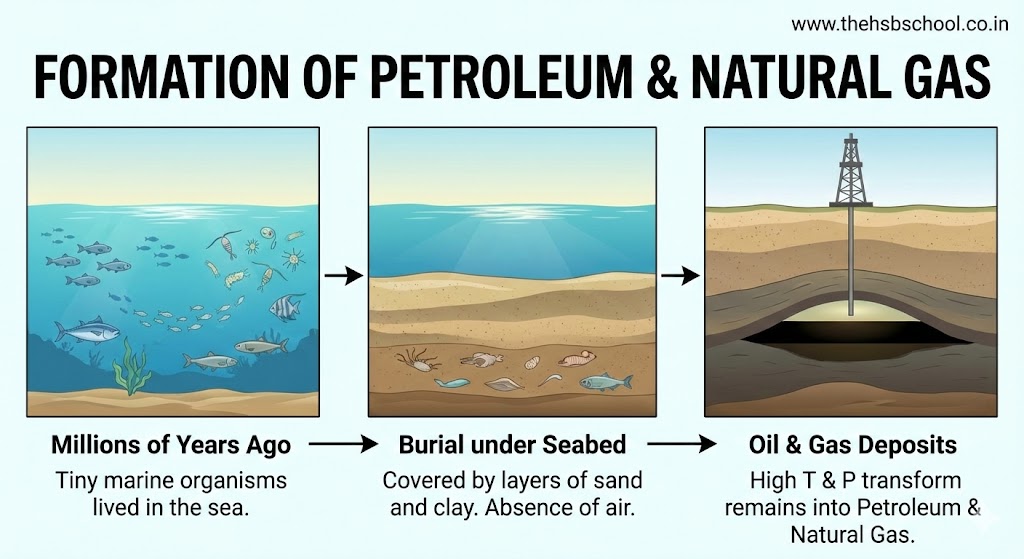
- Formation of Petroleum:
- Petroleum was formed from organisms living in the sea.
- As these organisms died, their bodies settled at the bottom of the sea and got covered with layers of sand and clay.
- Over millions of years, in the absence of air, high temperature, and high pressure transformed the dead organisms into petroleum and natural gas.
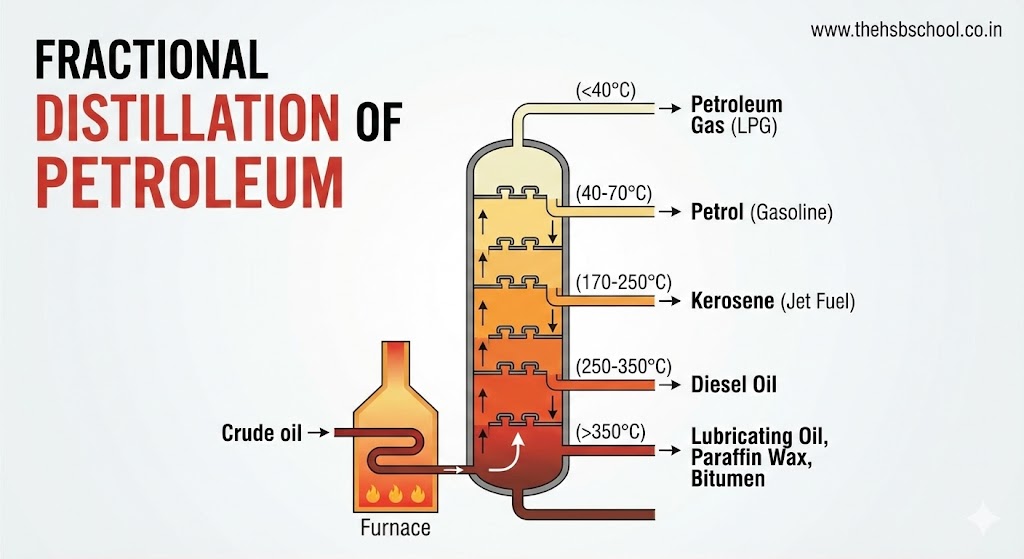
- Refining of Petroleum: Petroleum is a mixture of various constituents like petroleum gas, petrol, diesel, lubricating oil, paraffin wax, etc. The process of separating the various constituents/fractions of petroleum is known as refining. It is carried out in a petroleum refinery.
6. Constituents of Petroleum and their Uses (Important Table)
| Constituent of Petroleum | Uses |
| Petroleum Gas in Liquid form (LPG) | Fuel for home and industry. |
| Petrol | Motor fuel, aviation fuel, solvent for dry cleaning. |
| Kerosene | Fuel for stoves, lamps, and for jet aircraft. |
| Diesel | Fuel for heavy motor vehicles, electric generators. |
| Lubricating Oil | Lubrication (to reduce friction in machinery). |
| Paraffin Wax | Ointments, candles, Vaseline, etc. |
| Bitumen | Paints, road surfacing. |
7. Natural Gas
- Natural gas is a very important fossil fuel because it is easy to transport through pipes.
- It is stored under high pressure as Compressed Natural Gas (CNG).
- Advantages of CNG: It is a cleaner fuel (pollutes less), produces a lot of heat, and can be used directly for burning in homes and factories supplied through pipes.
- In India, vast reserves of natural gas are found in Tripura, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and in the Krishna Godavari delta.
8. Some Natural Resources are Limited (Conservation)
Fossil fuels take millions of years to form, and known reserves will last only a few hundred years. Moreover, burning these fuels is a major cause of air pollution and global warming. We must use them judiciously.
PCRA Guidelines: In India, the Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA) advises people on how to save petrol/diesel while driving:
- Drive at a constant and moderate speed.
- Switch off the engine at traffic lights or places where you have to wait.
- Ensure correct tyre pressure.
- Ensure regular maintenance of the vehicle.
🗣️ SECTION 2: SUBJECTIVE QUESTION AND ANSWERS – Coal and Petroleum Class 8
Q1. Define fossil fuels. Give two examples.
Ans: Fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources formed from the dead remains of living organisms (fossils) buried under earth for millions of years due to high temperature and pressure. Examples: Coal and Petroleum.
Q2. Describe how coal is formed from dead vegetation. What is this process called?
Ans: Millions of years ago, dense forests in low-lying wetland areas got buried under the soil due to natural processes like floods. As more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. Under high temperature and high pressure deeper inside the earth, these dead plants slowly got converted into coal. This slow process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called carbonisation.
Q3. Write the full form of CNG and LPG. Mention one use of each.
Ans:
- CNG: Compressed Natural Gas. Use: Used as a fuel for transport vehicles as it is cleaner.
- LPG: Liquefied Petroleum Gas. Use: Used as a fuel for homes and industry (cooking gas cylinders).
Q4. Name the products obtained by the destructive distillation of coal. Which one is the purest form of carbon?
Ans: The products obtained are Coke, Coal Tar, and Coal Gas. Coke is the purest form of carbon among these.
Q5. Explain the process of formation of petroleum.
Ans: Petroleum was formed from organisms living in the sea. As these organisms died, their bodies settled at the bottom of the sea and got covered with layers of sand and clay. Over millions of years, absence of air, high temperature, and high pressure transformed these dead organisms into petroleum and natural gas.
Q6. Why should we use fossil fuels judiciously?
Ans: We should use fossil fuels judiciously because:
- They are exhaustible resources and take millions of years to form. Their known reserves are limited.
- Burning fossil fuels causes air pollution, which is harmful to health.
- Burning them releases carbon dioxide, leading to global warming.
Q7. State the uses of a) Kerosene and b) Bitumen.
Ans:
a) Kerosene: Used as fuel for stoves, lamps, and for jet aircrafts.
b) Bitumen: Used in paints and for surfacing roads.
✅ SECTION 3: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) – Coal and Petroleum Class 8
1. Which of the following is an exhaustible natural resource?
a) Air
b) Sunlight
c) Water
d) Minerals
Correct Answer: d) Minerals
2. The slow process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called:
a) Oxidation
b) Carbonisation
c) Refining
d) Distillation
Correct Answer: b) Carbonisation
3. Which of the following is obtained from coal tar?
a) Petrol
b) Coke
c) Naphthalene balls
d) Bitumen
Correct Answer: c) Naphthalene balls
4. The purest form of carbon obtained from coal is:
a) Coal Tar
b) Coal Gas
c) Coke
d) Charcoal
Correct Answer: c) Coke
5. Petroleum is also known as:
a) Black Gold
b) White Gold
c) Liquid Silver
d) Black Diamond
Correct Answer: a) Black Gold
6. Which petroleum product is used for surfacing roads these days?
a) Coal tar
b) Coke
c) Bitumen
d) Paraffin wax
Correct Answer: c) Bitumen
7. The least polluting fuel for vehicles is:
a) Petrol
b) Diesel
c) Kerosene
d) CNG
Correct Answer: d) CNG
8. Petroleum was formed from organisms living in:
a) Forests
b) The Sea
c) Deserts
d) Mountains
Correct Answer: b) The Sea
9. The process of separating various constituents of petroleum is called:
a) Carbonisation
b) Distillation
c) Refining
d) Purification
Correct Answer: c) Refining
10. Which constituent of petroleum is used in jet aircrafts?
a) Petrol
b) Diesel
c) Kerosene
d) LPG
Correct Answer: c) Kerosene
11. PCRA stands for:
a) Petroleum Conservation Research Association
b) Petrol Coal Refining Association
c) Public Conservation Research Association
d) Pollution Control Research Association
Correct Answer: a) Petroleum Conservation Research Association
12. Which of these is NOT a fossil fuel?
a) Coal
b) Wood
c) Petroleum
d) Natural gas
Correct Answer: b) Wood (Wood is a biomass fuel, not a fossil fuel formed over millions of years under high pressure).
#Coal and Petroleum Class 8
