World War II (1939–1945) was more than just a war—it was a cataclysmic event that reshaped our world forever. This World War 2 Timeline Overview doesn’t just list dates—it reveals the hidden battles, the untold stories, and the shocking truths behind history’s deadliest conflict.
Table of Contents
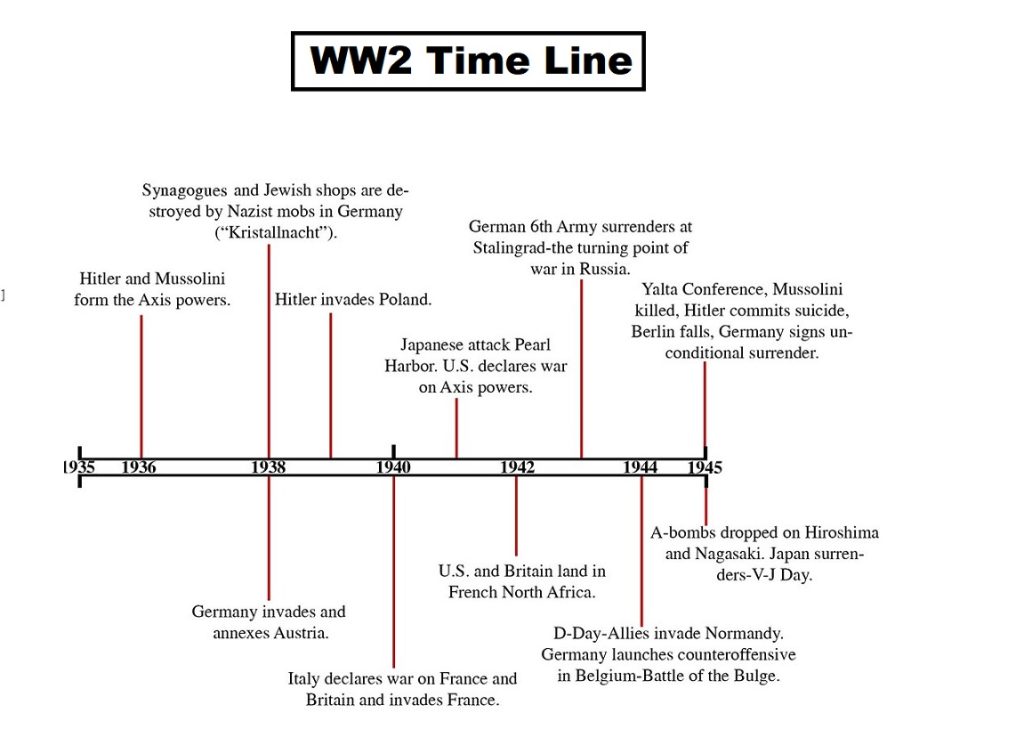
World War 2 Timeline Overview
1939 – The War Ignites: More Than Just Poland
September 1: Germany’s Blitzkrieg Onslaught
- Hitler unleashed Blitzkrieg (“lightning war”) on Poland.
- Coordinated tank-aircraft assaults smashed defenses.
- Warsaw suffered relentless civilian bombing.
- Britain & France declared war—but offered little real aid.
September 17: Stalin’s Secret Invasion
- USSR invaded Poland from the east under the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact.
- Poland was split between Hitler & Stalin.
The Winter War: Finland’s Miraculous Stand (Nov 1939–Mar 1940)
- Finnish ski troops ambushed Soviet tanks.
- “Molotov cocktails” were invented.
- Soviet casualties: 200,000+ vs Finland’s 25,000.
1940 – Hitler’s Blitzkrieg Dominates Europe
Operation Weserübung: Why Germany Invaded Scandinavia
- Secured Swedish iron ore.
- Gained U-boat bases to threaten Britain.
- Prevented Allied blockade of vital supplies.
The Fall of France: 6 Weeks to Collapse
- German tanks bypassed the Maginot Line.
- Allied communications broke down.
- France surrendered June 22.
Battle of Britain: The Few Who Saved Civilization
- 3,000 RAF pilots vs massive Luftwaffe.
- Radar gave Britain a crucial edge.
- 57 nights of the Blitz tested civilian resilience.
1941 – The War Goes Global
Operation Barbarossa: Hitler’s Fatal Mistake
- 3 million German troops invaded USSR.
- Harsh winter (-40°C) and overstretched supply lines broke the advance.
- Siberian reinforcements turned the tide at Moscow.
Pearl Harbor: The Attack That Backfired (Dec 7)
- Japan destroyed U.S. battleships but missed aircraft carriers.
- Awoke U.S. industrial might—the “sleeping giant.”
- Brought America fully into the war.

Siege of Leningrad: 872 Days of Starvation
- 1 million civilians died.
- People survived on wallpaper paste, leather, and bread rations.
- The “Road of Life” over frozen Lake Ladoga kept the city alive.
1942 – The Tide Turns
Battle of Midway: 5 Minutes That Changed the Pacific
- U.S. codebreakers predicted attack.
- Dive bombers sank 4 Japanese carriers.
- Japan’s naval dominance ended.
Stalingrad: Germany’s Breaking Point
- Bloodiest battle in history: 2 million casualties.
- Soviets encircled 6th Army; Hitler forbade retreat.
- Germany’s eastern offensive collapsed.
The Holocaust Accelerates
- Wannsee Conference approved the “Final Solution.”
- Gas chambers and extermination camps like Auschwitz industrialized mass murder.
1943 – Allies Strike Back
Kursk: The Greatest Tank Battle Ever
- 6,000 tanks clashed.
- Soviet defenses and deep minefields stopped Germany.
- From here, Germany was always retreating in the East.
Italian Campaign: Cracks in the Axis
- Allies invaded Sicily; Mussolini was deposed.
- Italy surrendered but Germans fought fiercely at Monte Cassino.
Warsaw Ghetto Uprising
- Jewish resistance fighters used tunnels, pistols, and Molotovs.
- Held off Nazi tanks for a month before being crushed.
1944 – Liberation of Europe
D-Day: The Greatest Gamble (June 6)
- 156,000 Allied troops landed on Normandy beaches.
- Omaha Beach saw horrific losses.
- French Resistance sabotaged German reinforcements.
Operation Market Garden: A Bridge Too Far
- Failed Allied attempt to seize Rhine bridges.
- 17,000 casualties and Dutch famine followed.
Battle of the Bulge: Hitler’s Last Throw (Dec 1944)
- Surprise German offensive in the Ardennes.
- Bastogne held by U.S. 101st Airborne.
- Germany exhausted its last reserves of men and fuel.
1945 – The Endgame & Dawn of the Atomic Age
Firebombing of Dresden (Feb)
- 25,000 civilians killed.
- Controversial as a cultural landmark was destroyed.
Battle of Berlin (April–May)
- Soviets stormed Berlin.
- Hitler and Eva Braun committed suicide.
- Germany surrendered May 7–8 (V-E Day).
Atomic Bombs: Necessary or War Crime?
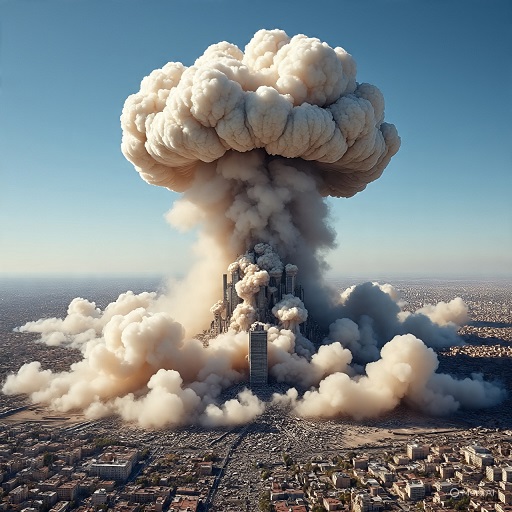

- Hiroshima (Aug 6):
- “Little Boy” uranium bomb.
- 80,000 killed instantly, ~140,000 by year’s end.
- Nagasaki (Aug 9):
- “Fat Man” plutonium bomb.
- 40,000 killed instantly, ~70,000 by year’s end.
- Long-term effects: radiation sickness, cancer, genetic damage.
Soviet Invasion of Manchuria (Aug 1945)
- 1 million Red Army troops crushed Japan’s Kwantung Army.
- Removed Japan’s last hope of negotiating peace.
- Forced Emperor Hirohito’s surrender.
Japan Surrenders (Sept 2, 1945)
- Signed aboard USS Missouri.
- WWII officially ended.
Aftermath: A World Remade
The Human Cost
- 70+ million dead worldwide.
- Holocaust murdered 6 million Jews.
- Millions displaced across continents.
A New World Order
- United Nations founded in 1945.
- U.S. and USSR emerged as rival superpowers → Cold War.
- Colonial empires rapidly collapsed.
Technological Legacy
- Jet engines, rockets, nuclear power.
- Early computers (codebreaking at Bletchley Park).
- Warfare changed forever.
Conclusion
This World War 2 Timeline Overview shows that the war was not only fought on battlefields—it was won through intelligence, supply chains, resilience, and human endurance. Every date reveals a story of sacrifice, tragedy, and survival that shaped the modern world. By studying this World War 2 Timeline Overview, we gain a deeper understanding of how those events continue to influence global history today.
Enjoyed this topic?
If you’re curious to learn more about science, don’t miss our other exciting blogs:
- What is Gravity?
- What is Electricity?
- What Causes Earthquakes?
- Why is the Sky Blue?
- How Do Plants Grow?
…and many more fascinating science topics!
