Reproduction in Animals Class 8 : A complete study guide for CBSE/NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 9, Reproduction in Animals. Includes detailed revision notes, definitions of sexual and asexual reproduction, solved subjective questions, and practice MCQs.

Table of Contents
📘 SECTION 1: Reproduction in Animals Class 8 – REVISION NOTES
1. Introduction to Reproduction
- Definition: Reproduction is the biological process by which existing organisms produce new individuals (offspring) of their own kind.
- Importance: It is essential for the continuation of species generation after generation. It prevents a species from becoming extinct.
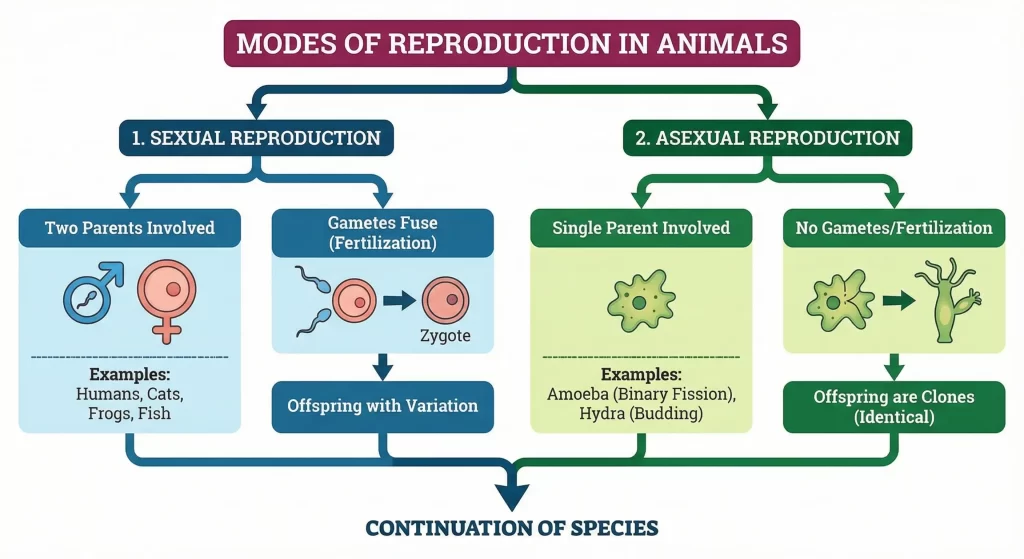
- Modes of Reproduction: There are two main modes:
- Sexual Reproduction: Involves the fusion of male and female gametes.
- Asexual Reproduction: Involves only a single parent; gametes are not produced.
2. Sexual Reproduction
- Gametes: These are reproductive cells.
- Male Gamete: Called sperm. Produced by testes. It is a single cell with a head, middle piece, and a tail (for movement).
- Female Gamete: Called ovum or egg. Produced by ovaries. It is also a single cell.
- Fertilization: The process of fusion of the sperm and ovum is called fertilization.
- When sperm comes in contact with an egg, one sperm may fuse with the egg.
- The nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus.
- The fertilized egg is called a Zygote.
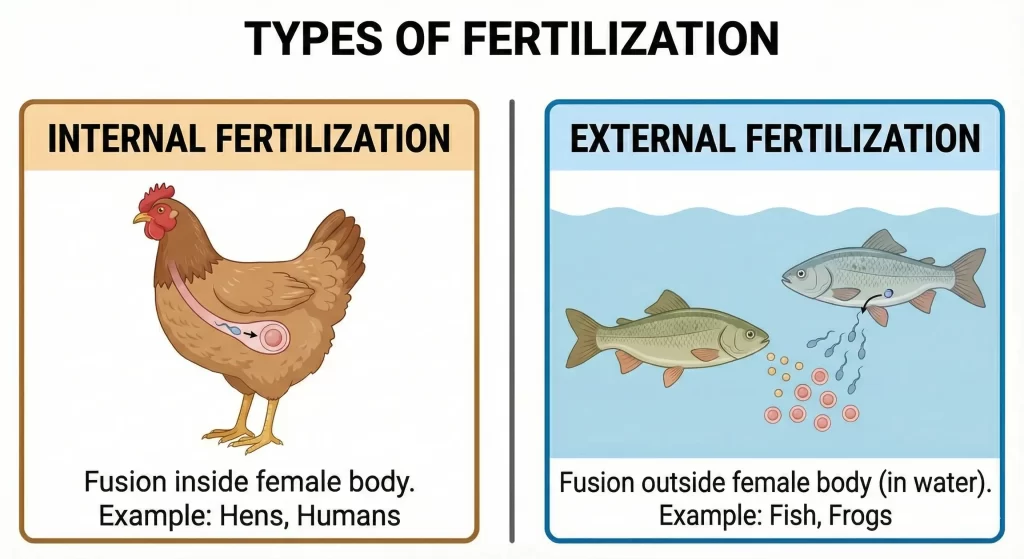
3. Types of Fertilization
- Internal Fertilization: Fertilization takes place inside the female body.
- Examples: Humans, cows, dogs, hens.
- External Fertilization: Fertilization takes place outside the female body (usually in water). The female lays hundreds of eggs, and the male deposits sperms over them.
- Examples: Fish, frogs, starfish.
4. Development of Embryo (in Humans)
- Zygote formation: Fertilization results in a zygote in the oviduct (fallopian tube).
- Embryo stage: The zygote divides repeatedly to form a ball of cells. This structure is called an embryo. It travels down and gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for development.
- Foetus stage: The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts (hands, legs, head, eyes, etc.) can be identified is called a foetus.
- Birth: When the development of the foetus is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
5. Viviparous and Oviparous Animals
- Viviparous Animals: Animals that give birth to young ones. Examples: Humans, cows, cats.
- Oviparous Animals: Animals that lay eggs. The young ones later hatch from these eggs. Examples: Hens, frogs, lizards, butterflies.
6. Life Cycle and Metamorphosis
- In some animals, the young ones look very different from the adults (e.g., silkworm, frog).
- Metamorphosis: The drastic change which transforms a larva into an adult is called metamorphosis.
- Frog Life Cycle: Egg → Tadpole (Larva) → Froglet → Adult Frog.
7. Asexual Reproduction
This mode is common in very small animals or microorganisms.
- Budding: A new individual develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site.
- Example: Hydra. Small bulges (buds) appear on the body, which develop into tiny hydras and eventually detach from the parent.
- Binary Fission: An organism reproduces by dividing into two individuals.
- Example: Amoeba. It is a single-celled organism. It begins reproduction by the division of its nucleus into two nuclei, followed by the division of its body into two, each part receiving a nucleus.
🗣️ SECTION 2: Reproduction in Animals Class 8 – SUBJECTIVE QUESTION AND ANSWERS
Q1: What is fertilization? Differentiate between internal and external fertilization.
Answer:
Fertilization is the process of the fusion of male gamete (sperm) and female gamete (ovum) to form a zygote.
| Internal Fertilization | External Fertilization |
| The fusion of gametes takes place inside the female body. | The fusion of gametes takes place outside the female body (usually in water). |
| The female lays fertilized eggs or gives birth to young ones. | The female discharges unfertilized eggs. |
| Examples: Humans, hens, cows. | Examples: Frogs, fish. |
Q2: Differentiate between a zygote and a foetus.
Answer:
- Zygote: It is the single cell formed after the fusion of the sperm and the egg (fertilization). It is the beginning of a new individual.
- Foetus: It is a multicellular stage of development that follows the embryo stage. In a foetus, all major body parts (like limbs, head, eyes) can be identified.
Q3: Explain the process of binary fission with an example.
Answer:
Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a single-celled parent organism divides into two equal parts, each growing into a new individual.
- Example – Amoeba: Amoeba is a single-celled organism. During reproduction, first, its nucleus divides into two daughter nuclei. Then, the cytoplasm divides into two parts, each containing a nucleus. Finally, two daughter amoebae are formed from one parent amoeba.
Q4: How is the development of a chick different from the development of a human baby?
Answer:
- Human: Fertilization is internal. The zygote develops into an embryo and then a foetus inside the mother’s uterus. The mother gives birth to a fully developed baby (Viviparous).
- Chick (Hen): Fertilization is internal. Soon after fertilization, the zygote divides repeatedly and travels down the oviduct. As it travels, many protective layers (the hard shell) are formed around it. The hen lays the egg. The embryo develops into a chick outside the mother’s body inside the eggshell (Oviparous). The hen sits on the eggs to provide warmth for development.
Q5: Define metamorphosis. Give two examples.
Answer:
Metamorphosis is the process of transformation of a larva into an adult through drastic changes in structure and appearance during the life cycle of an animal.
- Examples: The transformation of a tadpole into a frog, and a caterpillar into a butterfly.
✅ SECTION 3: Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs)
1. The fusion of sperm and egg results in the formation of a:
a) Gamete
b) Zygote
c) Embryo
d) Foetus
Correct Answer: b) Zygote
2. In humans, fertilization occurs in the:
a) Ovary
b) Uterus
c) Oviduct (Fallopian tube)
d) Vagina
Correct Answer: c) Oviduct (Fallopian tube)
3. Which of the following is an example of a viviparous animal?
a) Frog
b) Sparrow
c) Cow
d) Butterfly
Correct Answer: c) Cow
4. Asexual reproduction involving the formation of buds occurs in:
a) Amoeba
b) Paramecium
c) Hydra
d) Human
Correct Answer: c) Hydra
5. The stage of the embryo in which all body parts can be identified is called the:
a) Zygote
b) Egg
c) Foetus
d) Larva
Correct Answer: c) Foetus
6. Metamorphosis is observed in which of the following?
a) Humans
b) Cats
c) Frogs
d) Hens
Correct Answer: c) Frogs
7. The number of modes of reproduction in animals is:
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
Correct Answer: b) Two (Sexual and Asexual)
