🌿 CLASS 6 SCIENCE CHAPTER 9 NOTES
The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
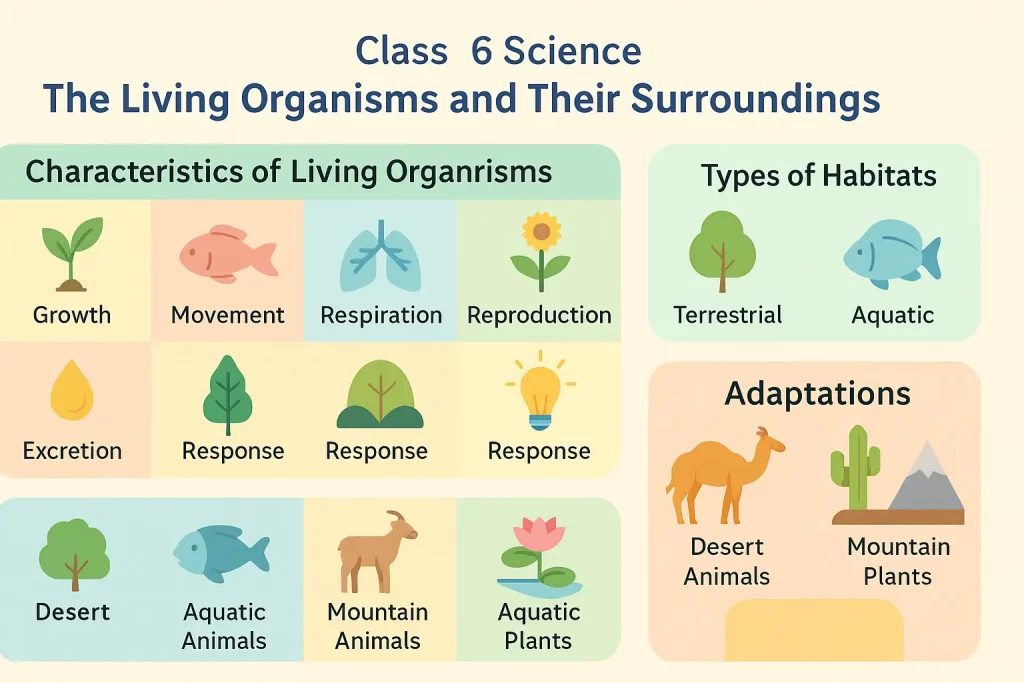
Table of Contents
⭐ 1. Characteristics of Living Things
Class 6 Science Chapter 9: Living organisms show the following features:
1. Growth
Living things grow in size.
Plants → grow throughout life
Animals → grow until a certain age
2. Movement
Plants: bending toward light, opening/closing flowers
Animals: walking, running, flying
3. Need Food
All living things need food to grow, get energy, repair body parts.
4. Respiration
Living organisms breathe:
- Humans → lungs
- Fish → gills
- Earthworm → skin
- Insects → spiracles
5. Respond to Stimuli (Sensitivity)
Living organisms respond to changes.
Example:
- Touch-me-not folds leaves
- Eyes blink in bright light
6. Excretion
Removal of waste
- Humans → urine, sweat
- Plants → gum, resin
7. Reproduction
Living things produce young ones
Plants reproduce by seeds, stems, roots
8. Adaptation
Special features that help plants & animals survive in their environment.
9. Life Cycle
Living beings have a life span (birth → growth → death).
⭐ 2. What Is Habitat?
A habitat is the natural home of an organism.
Types of Habitats:
- Terrestrial (Land)
- Mountains
- Deserts
- Forests
- Grasslands
- Aquatic (Water)
- Freshwater (ponds, rivers)
- Marine (sea/ocean)
⭐ 3. Adaptation and Types
Adaptation = special features that help plants/animals survive.
A. Desert Animals Adaptations:
- Thick skin
- Less sweating
- Camel stores fat in hump
- Can live without water for many days
B. Desert Plants Adaptations:
- Long roots
- Leaves reduced to spines
- Thick stems to store water (cactus)
C. Mountain Animals Adaptations:
- Thick fur
- Long hair
- Strong hooves (yak, mountain goat)
D. Mountain Plants Adaptations:
- Conical shape
- Needle-like leaves (pine trees)
E. Aquatic Animals Adaptations:
- Streamlined body (fish)
- Gills (fish)
- Fins & tail for movement
- Dolphins/whales breathe air through blowholes
F. Aquatic Plants Adaptations:
- Air cavities (lotus)
- Floating leaves
- Thin, ribbon-like leaves in underwater plants
⭐ 4. Environment and Organisms
Environment = all living + non-living things.
Living and non-living things depend on each other for:
- Food
- Air
- Water
- Shelter
📘 IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS – Class 6 Science Chapter 9
✅ 1 Mark Questions
1. What is a habitat?
The natural home of an organism.
2. Define adaptation.
Special features that help organisms survive.
3. Name a freshwater plant.
Lotus.
4. How do fish breathe?
Using gills.
5. What are organisms that live on land called?
Terrestrial organisms.
✅ 2 Mark Questions
6. What are the two main types of habitats?
Terrestrial & Aquatic.
7. How is a camel adapted to live in the desert?
- Long legs
- Thick skin
- Stores fat in hump
- Can survive without water for days.
8. What is respiration?
Process of taking in oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide.
✅ 3 Mark Questions
9. How do desert plants survive in dry conditions?
- Leaves become spines
- Thick stems store water
- Long roots absorb water from deep soil
10. Explain the characteristics of living organisms.
- Grow
- Need food
- Move
- Reproduce
- Respond
- Excrete
- Respire
11. How are aquatic plants adapted?
- Air cavities
- Broad leaves
- Weak stems
- Ribbon-like leaves for underwater flow
✅ 5 Mark Questions
12. Explain the adaptations in animals living in mountains, deserts, and water.
Mountains:
- Thick fur
- Long hair
- Strong hooves
Deserts:
- Less sweat
- Water storage (camel)
- No leaves (cactus spines)
Water animals:
- Streamlined body
- Gills
- Fins
13. Describe terrestrial and aquatic habitats with examples.
Terrestrial: land (forest, grassland, desert)
Examples: lion, camel, snakes
Aquatic: water (pond, river, ocean)
Examples: fish, dolphins, crabs
⭐ HOTS Questions
14. Why do dolphins come to the surface to breathe?
Because they have lungs, not gills.
15. Why do mountain trees have needle-like leaves?
To reduce loss of water and withstand snowfall.
