Getting to Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Know Plants (NCERT)
Table of Contents
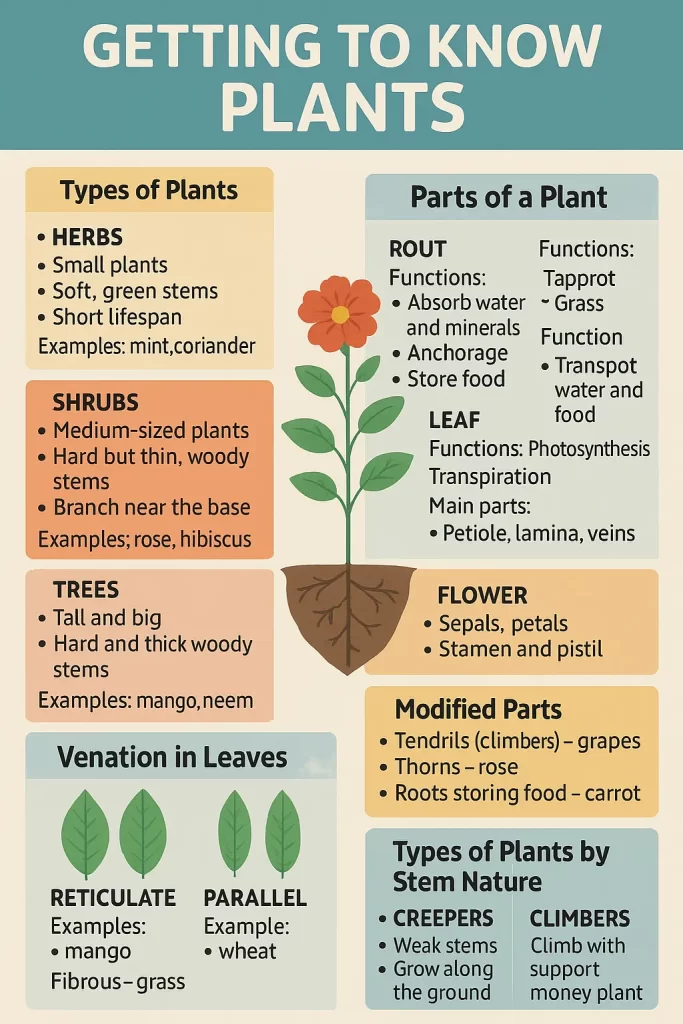
⭐ 1. Types of Plants
Class 6 Science Chapter 7 : Plants are classified into three main groups:
A. Herbs
- Small plants
- Soft, green stems
- Short lifespan
Examples: mint, coriander, tomato
B. Shrubs
- Medium-sized plants
- Hard but thin, woody stems
- Branch out near the base
Examples: rose, hibiscus, cotton
C. Trees
- Tall and big
- Hard and thick woody stems
- Branch higher above the ground
Examples: mango, neem, banyan
⭐ 2. Parts of a Plant (Root, Stem, Leaf, Flower)
Class 6 Science Chapter 7:
A. Root
Functions:
- Absorbs water and minerals from the soil
- Anchors the plant
- Stores food (in some plants like carrot, radish)
Types of Roots:
- Taproot – one main root with small branches
Examples: mango, carrot, mustard - Fibrous Root – many thin roots from the base
Examples: wheat, grass, onion
B. Stem
Functions:
- Supports the plant
- Transports water and food
- Carries water from root → leaves
- Carries food from leaves → other parts
C. Leaf
Parts of a Leaf:
- Petiole: leaf stalk
- Lamina: broad part of leaf
- Veins: small lines that carry water
- Midrib: thick central vein
Functions of Leaf:
- Makes food (photosynthesis)
- Exchanges gases
- Transpiration (loss of water through leaves)
Photosynthesis:
Plants prepare food using:
- Sunlight
- Chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
They produce oxygen during photosynthesis.
D. Flower
It is the reproductive part of a plant.
Parts of a Flower:
- Sepals – green, protect bud
- Petals – colored, attract insects
- Stamens – male part (anther + filament)
- Pistil/Carpel – female part (stigma, style, ovary)
⭐ 3. Venation in Leaves
Class 6 Science Chapter 7
- Reticulate: net-like veins
Example: mango, rose - Parallel: veins run parallel
Example: wheat, banana
⭐ 4. Modified Parts of Plants
Class 6 Science Chapter 7
- Tendrils (climbers) – help plant climb (grapes)
- Thorns – protect plant (rose)
- Roots storing food – beetroot, carrot
⭐ 5. Types of Plants by Stem Nature
Class 6 Science Chapter 7
- Creepers: weak stems, grow along ground (pumpkin)
- Climbers: climb with support (money plant)
📘 Class 6 Science Chapter 7 : Important Questions & Answers – Chapter 7
✅ A. Very Short Answer (1 Mark)
1. Name the three types of plants.
Herbs, shrubs, trees.
2. What are veins?
Lines on the leaf that carry water and food.
3. What is the function of roots?
To absorb water and minerals.
4. Give one example of a herb.
Mint.
5. Which pigment helps in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll.
✅ B. Short Answer (2 Marks)
6. What are herbs? Give two examples.
Small plants with green, soft stems.
Examples: coriander, mint.
7. Differentiate between taproot and fibrous root.
- Taproot: one main root → carrot
- Fibrous: many thin roots → grass
8. What is transpiration?
Loss of water from leaves as water vapor.
✅ C. Short Answer (3 Marks)
9. Explain the structure of a leaf.
A leaf has:
- Petiole (stalk attaching leaf to stem)
- Lamina (broad flat part)
- Veins (network carrying water & food)
- Midrib (main vein)
10. Write three functions of the stem.
- Supports plant
- Carries water from root to leaves
- Carries food from leaves to other parts
11. What are climbers and creepers? Give examples.
- Climbers: climb with support (money plant, pea)
- Creepers: grow along the ground (pumpkin, watermelon)
✅ D. Long Answer (5 Marks)
12. Describe the parts of a flower.
- Sepals: protect the bud
- Petals: attract insects
- Stamen: male reproductive part
- Anther
- Filament
- Pistil: female reproductive part
- Stigma
- Style
- Ovary
13. Explain photosynthesis. What materials are needed?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make food in leaves.
Plants need:
- Sunlight
- Chlorophyll
- Water
- Carbon dioxide
It produces oxygen and glucose.
✅ E. HOTS (Higher Order Thinking)
14. Why do leaves appear green?
Because they contain chlorophyll, which reflects green light.
15. Why do plants with fibrous roots prevent soil erosion?
Fibrous roots spread out and hold soil tightly.
16. Why do climbers have weak stems?
Because they use external support to grow upward.
