Complete notes and important questions for NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 5 – Separation of Substances. Learn methods of separation like handpicking, winnowing, sieving, filtration, evaporation, sedimentation, decantation, and more. Perfect for CBSE Class 6 students, revision, and exam preparation.
Class 6 Science Chapter 5: Separation of Substances (NCERT)
Table of Contents
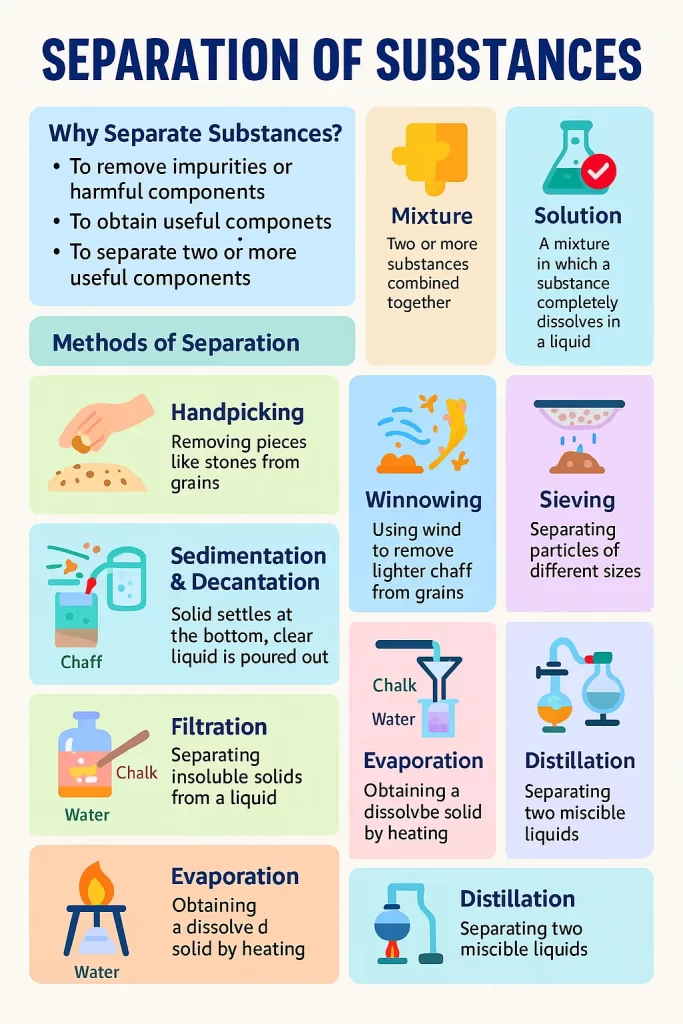
⭐ 1. Why Do We Need to Separate Substances?
Class 6 Science Chapter 5:
Separation is done to:
- Remove harmful or unwanted substances
- Obtain useful substances
- Remove impurities
- Separate two or more useful components
- Improve quality and purity
Example:
- Removing stones from rice
- Separating tea leaves from tea
⭐ 2. Methods of Separation
Class 6 Science Chapter 5:
A. Handpicking
Used to separate large impurities like stones from grains.
B. Threshing
Used to separate grain from stalk.
Done by:
- Beating
- Machines
- Trampling by animals
C. Winnowing
Used to separate lighter and heavier components.
- Light chaff → blows away
- Heavy grain → falls down
D. Sieving
Used to separate particles of different sizes.
Examples:
- Flour sieving
- Sand and gravel separation
E. Sedimentation
When heavier insoluble solids settle at the bottom.
F. Decantation
Clear liquid is poured out after sedimentation.
G. Filtration
Used to separate insoluble solids from liquids using filter paper.
H. Evaporation
Used to obtain a solid dissolved in a liquid by heating.
Example:
- Getting salt from seawater.
I. Condensation
Converting water vapor into water.
J. Distillation
Used to separate two miscible liquids (very simple intro).
K. Loading
Adding alum to speed up sedimentation (impure water treatment).
L. Chromatography (higher concept)
Used to separate different colours from a mixture (inking experiment).
⭐ 3. Soluble and Insoluble Substances
Soluble:
Salt, Sugar
Insoluble:
Chalk, Sand, Oil
⭐ 4. Mixtures & Solutions
Mixture:
Two or more substances physically mixed (no chemical change).
Solution:
A mixture where a substance dissolves completely in a liquid.
- Solute: substance that dissolves
- Solvent: liquid in which solute dissolves
📘 Important Questions & Answers – Chapter 5
Class 6 Science – Separation of Substances
✅ A. Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. What is a mixture?
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances.
2. What is handpicking?
Manually removing unwanted particles from food grains.
3. Name one method to separate tea leaves from tea.
Filtration.
4. What is evaporation?
Process of converting liquid into vapour by heating.
5. What is winnowing used for?
Separating lighter chaff from heavier grains.
✅ B. Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
6. Why do we separate substances?
To remove impurities, obtain useful materials, improve quality, and separate components of a mixture.
7. What are soluble and insoluble substances?
- Soluble: dissolve in water (salt, sugar).
- Insoluble: do not dissolve in water (sand, oil).
8. What is sedimentation and decantation?
- Sedimentation: heavier solids settle.
- Decantation: clear liquid is poured off.
9. What is sieving? Give example.
Sieving separates particles of different sizes.
Example: sand and gravel.
✅ C. Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
10. Explain filtration with an example.
Filtration separates insoluble solids from liquids using filter paper.
Example: separating chalk powder from water.
11. How is salt obtained from seawater?
- Seawater is collected in shallow pits.
- Sunlight causes evaporation.
- Salt remains as solid.
12. What is winnowing and when is it used?
Using wind or air to separate lighter materials from heavier ones.
Used by farmers to separate chaff from grains.
✅ D. Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
13. Describe any four methods of separation with examples.
Handpicking:
Removing stones from rice.
Winnowing:
Separating chaff from wheat.
Sieving:
Separating bigger particles from smaller ones.
Evaporation:
Getting salt from seawater.
14. Describe the process of separating muddy water using sedimentation, decantation, and filtration.
- Allow muddy water to stand.
- Mud settles (sedimentation).
- Pour clear water (decantation).
- Filter to remove remaining particles (filtration).
✅ E. HOTS (Higher Order Thinking)
15. Why can’t we separate salt from water using filtration?
Salt dissolves completely, forming a solution, so filter paper cannot trap it.
16. Why does sand settle faster than clay in water?
Sand particles are heavier and larger, so they settle quickly.
17. Why is distillation not taught as a basic method?
It requires special equipment and heating; it’s more advanced for Class 6.
