Class 6 Science Chapter 12 : Electricity and Circuits
Clear and complete notes for NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuits. Learn about electric cells, circuits, bulbs, switches, conductors, insulators, and safety rules. Includes diagrams and important question–answers for Class 6 exam preparation.
Table of Contents
⭐ 1. What is Electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy that makes:
- Bulbs glow
- Fans run
- Machines work
Sources of electricity:
- Electric cell (battery)
- Power stations
- Solar cells
⭐ 2. Electric Cell (Battery)
An electric cell has:
- Positive terminal (+)
- Negative terminal (–)
How does a cell work?
It converts chemical energy → electrical energy.
Symbol:
- A longer line → positive
- A shorter line → negative
⭐ 3. Battery
Two or more cells connected together make a battery.
Example: TV remote uses 2 cells (AA or AAA).
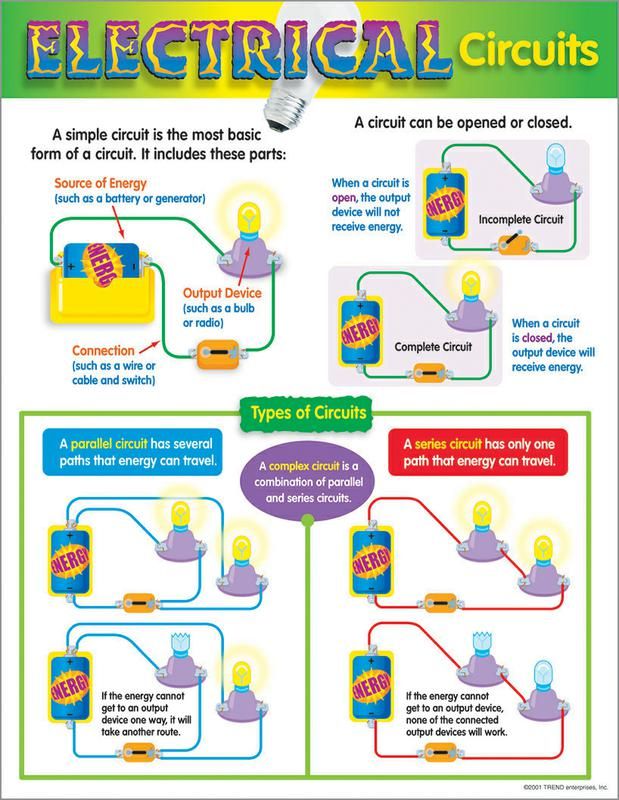
⭐ 4. Electric Circuit
A pathway through which electric current flows.
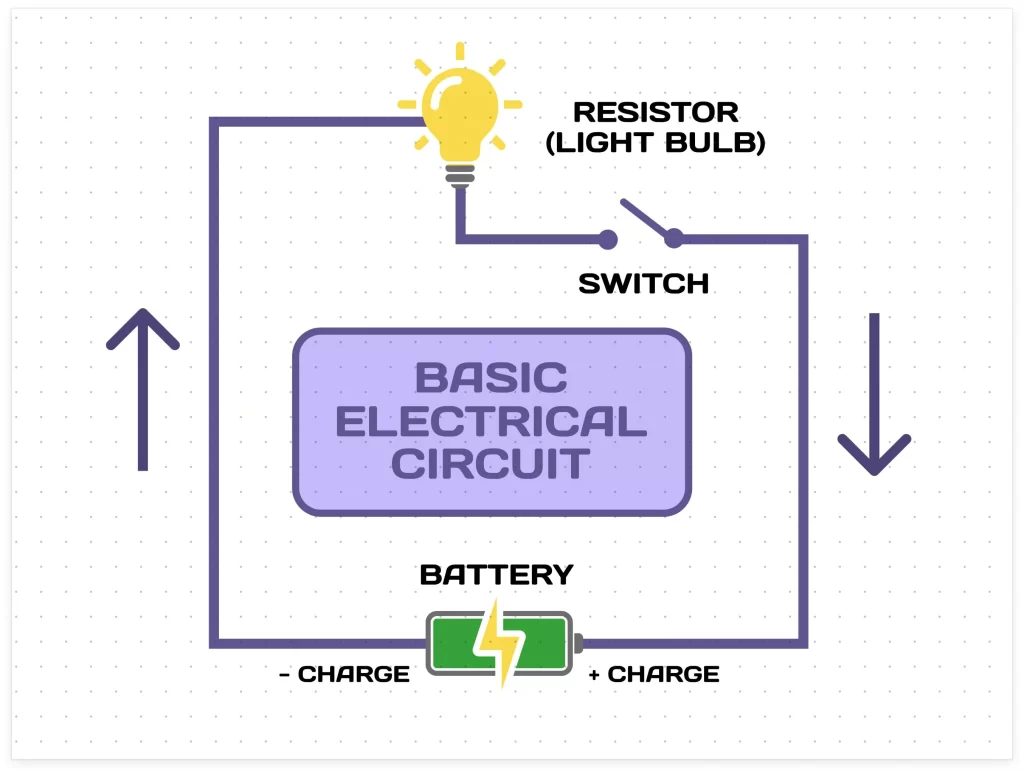
Components of a circuit:
- Cell / battery
- Bulb
- Wires
- Switch
Types of Circuits
1. Open Circuit
- Switch OFF
- Current does not flow
- Bulb does NOT glow
2. Closed Circuit
- Switch ON
- Current flows
- Bulb glows
⭐ 5. Electric Bulb
A bulb has:
- Filament → thin wire inside the bulb
- Base → connects to holder
When current passes → filament heats → glows.
If filament breaks → bulb fuses.
⭐ 6. Conductors and Insulators
Conductors
Allow electric current to pass.
Examples: copper, aluminium, iron, water (impure).
Insulators
Do NOT allow current to pass.
Examples: rubber, plastic, wood, glass.
⭐ 7. Switch
A device that opens or closes a circuit.
- OFF → open circuit (no glow)
- ON → closed circuit (bulb glows)
⭐ 8. Testing Materials
Materials can be tested by placing them in a circuit to see whether the bulb glows.
⭐ 9. Safety with Electricity
- Never touch switches with wet hands
- Do not insert metal objects in sockets
- Use only insulated wires
📘 IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS – Class 6 Science Chapter 12
✅ 1 Mark Questions
1. What is an electric circuit?
A path through which electric current flows.
2. What are the terminals of a cell?
Positive (+) and Negative (−).
3. What is a conductor?
A material that allows current to pass through it.
4. Name two insulators.
Rubber, wood.
5. What happens if the filament breaks?
The bulb gets fused and does not glow.
✅ 2 Mark Questions
6. What is the difference between an open and closed circuit?
- Open: current does not flow → bulb doesn’t glow
- Closed: current flows → bulb glows
7. What is the function of a switch?
To open or close the electrical circuit.
8. Why should we not touch electric switches with wet hands?
Because water conducts electricity → risk of shock.
✅ 3 Mark Questions
9. Explain how a bulb glows.
- Electric current passes through filament
- Filament gets heated
- It starts glowing
10. Write differences between conductors and insulators.
| Conductors | Insulators |
|---|---|
| Let current pass | Do not let current pass |
| Example: copper | Example: plastic |
11. Draw and explain a simple electric circuit.
(You can describe this for students)
- Cell → wire → bulb → wire → back to cell
- The circuit must be closed for the bulb to glow.
✅ 5 Mark Questions
12. Describe the structure of an electric bulb and how it works.
- Glass cover
- Filament inside
- Two terminals
- When current flows, filament heats up and glows
- If filament breaks → bulb fused
13. Explain with examples: conductors, insulators, and their uses in everyday life.
Conductors:
- Copper wires → carry electric current
- Aluminium wires → used in electric lines
Insulators:
- Plastic coating on wires
- Rubber handles of tools
- Wooden switches in old houses
Their function: to protect humans from electric shock.
⭐ HOTS Questions – Class 6 Science Chapter 12
14. Why is the base of an electric bulb made of metal?
Because metal conducts electricity from the circuit to the filament.
15. Why is a tester used?
To check if a material conducts electricity.
16. Why do birds sitting on electric wires not get shocked?
Because they are only touching the wire at one point → no complete circuit.
# Class 6 Science Chapter 12
