Prepare for Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 exams with these notes, questions, and answers for Chapter 8: Cell Structure and Functions Class 8. Covers discovery, shapes, parts of the cell, and comparisons.
Table of Contents
📘 Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 SECTION 1: REVISION NOTES
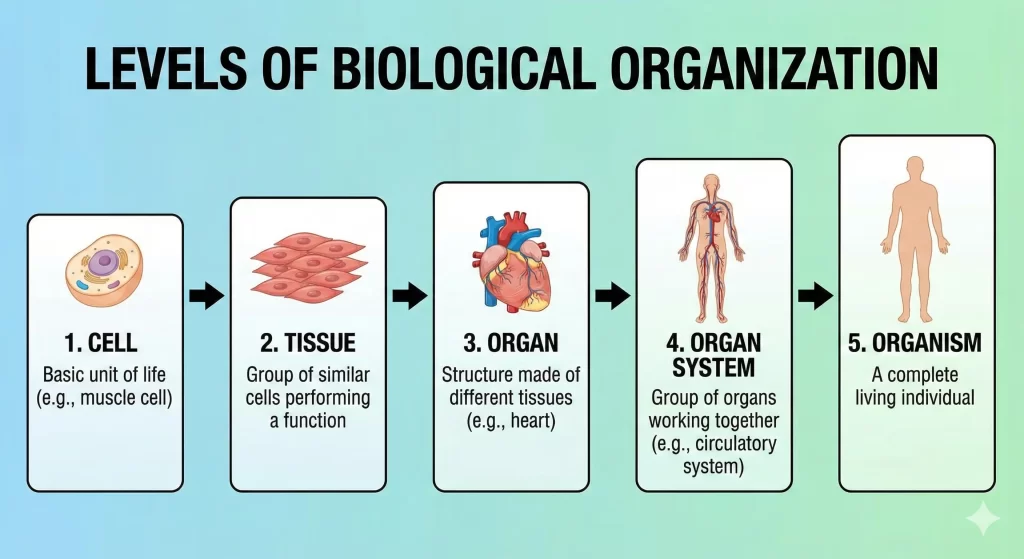
1. Introduction to the Cell
- Discovery: Cells were first observed in cork slices by Robert Hooke in 1665. He observed honeycomb-like structures and termed them “cells”.
- Definition: The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. All living organisms are made up of cells.
2. Variety in Cells
Cells vary in number, shape, and size in different organisms.
- Number of Cells:
- Unicellular Organisms: Made of a single cell capable of performing all life functions (e.g., Amoeba, Paramecium, Bacteria).
- Multicellular Organisms: Made of more than one cell. Cells are specialized to perform specific functions (e.g., Humans, Trees, Elephants).
- Shape of Cells: Cells have diverse shapes adapted to their functions.
- Some have irregular/changing shapes (e.g., Amoeba, White Blood Cells in humans).
- Some have fixed shapes like spherical (Red Blood Cells), spindle-shaped (Muscle cells), or long and branched (Nerve cells).
- Size of Cells:
- The smallest cell is a bacterium (0.1 to 0.5 micrometer).
- The largest cell is the egg of an ostrich (170 mm × 130 mm).
3. Structure of a Cell
A typical cell consists of three main parts:
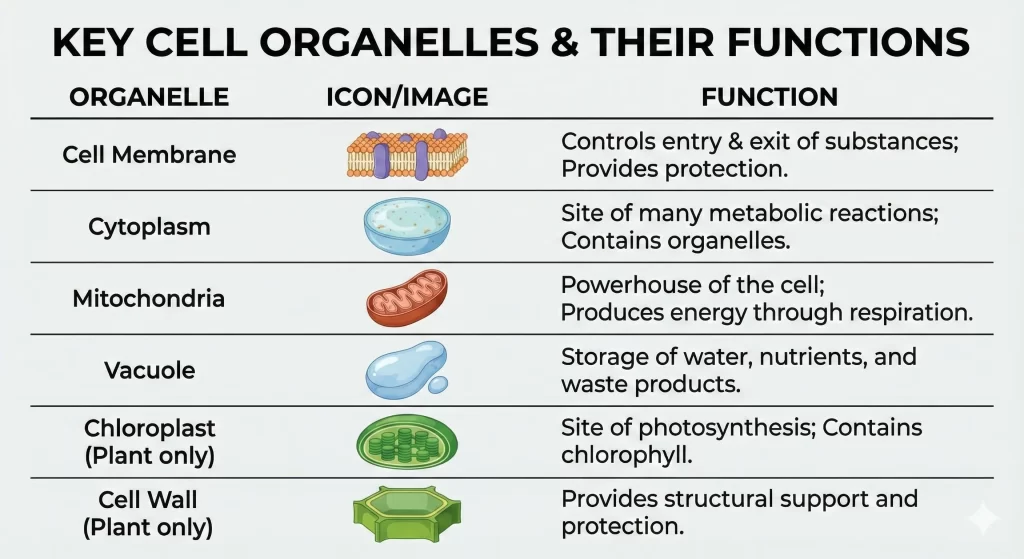
- Cell Membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- A. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane):
- The outer boundary of the cell.
- It is porous and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- It gives shape to the cell.
- Cell Wall (In Plants only): An additional, thick, rigid outer layer outside the cell membrane in plant cells, bacteria, and fungi. It provides protection against temperature variations, high wind speed, and atmospheric moisture.
- B. Cytoplasm:
- The jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus.
- Various cell organelles (like mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi bodies) are suspended in the cytoplasm.
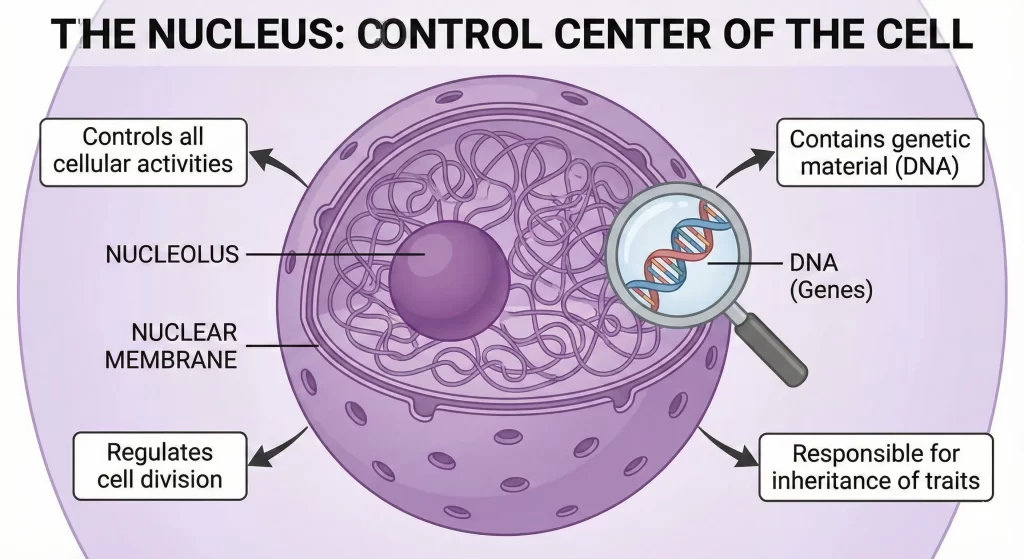
- C. Nucleus:
- The central, dense, spherical body located in the center of the cell. It is the “control center” of the cell.
- Nuclear Membrane: A porous double membrane separating the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
- Nucleolus: A smaller, spherical body inside the nucleus.
- Chromosomes: Thread-like structures visible during cell division. They carry genes and help in the inheritance or transfer of characters from parents to offspring.
4. Other Cell Organelles (Brief Overview)
- Mitochondria: The “powerhouse” of the cell; provides energy.
- Vacuoles: Blank-looking structures in the cytoplasm used for storage. Plant cells usually have a single large central vacuole; animal cells have smaller vacuoles.
- Plastids (In Plants only): Colored bodies in the cytoplasm of plant cells.
- Chloroplasts: Green plastids containing chlorophyll, essential for photosynthesis.
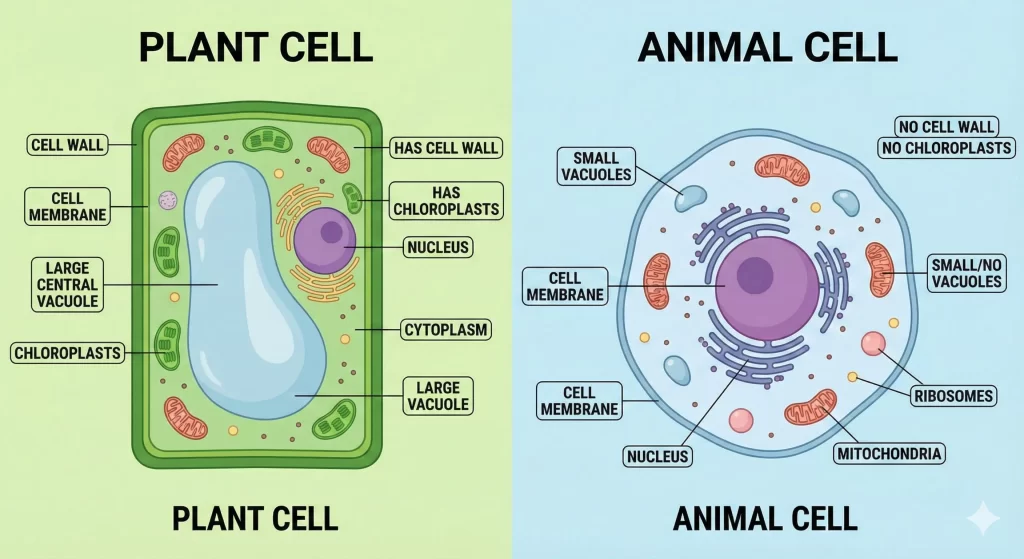
5. Comparison: Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Cell Membrane | Present | Present |
| Nucleus | Present (often shifted to side due to large vacuole) | Present (usually central) |
| Plastids/Chloroplasts | Present | Absent |
| Vacuoles | Large, central vacuole | Small and usually absent |
| Shape | Generally fixed, rigid rectangular shape | Irregular shape |
🗣️ Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 SECTION 2: SUBJECTIVE QUESTION AND ANSWERS
Q1: Define the cell. Who discovered it?
Answer:
A cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 when observing a thin slice of cork under a crude microscope.
Q2: Why is the nucleus considered the most important part of the cell?
Answer:
The nucleus is considered the most important part because it acts as the “control center” of the cell. It regulates all major cellular activities and metabolic processes. It also contains thread-like structures called chromosomes, which carry genes responsible for transferring hereditary characteristics from parents to offspring.
Q3: Differentiate between unicellular and multicellular organisms with examples.
Answer:
- Unicellular Organisms: These are organisms made up of only a single cell. That single cell performs all necessary life functions like digestion, respiration, and reproduction. Examples: Amoeba, Paramecium.
- Multicellular Organisms: These are organisms made up of more than one cell. Different groups of cells (tissues/organs) are specialized to perform specific functions. Examples: Humans, Mango tree, Cat.
Q4: Why do plant cells have a cell wall, but animal cells do not?
Answer:
Plant cells have an additional rigid outer layer called the cell wall outside the cell membrane. Since plants cannot move to seek shelter, the cell wall provides necessary protection against harsh environmental conditions like temperature variations, high wind speeds, and atmospheric moisture. Animal cells do not need this rigid structure as they are mobile and have skeletal systems for support.
Q5: What are genes and where are they found?
Answer:
Genes are the units of inheritance in living organisms. They control the transfer of a hereditary characteristic from parents to offspring. Genes are located on chromosomes, which are found inside the nucleus of the cell.
Q6: Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
(Note: Students should draw a long, branched neuron structure).
Function: The nerve cell (neuron) is long and branched. It is specialized to receive and transfer messages (nerve impulses), thereby helping to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body.
✅ Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 SECTION 3: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs)
1. The term “cell” was coined by:
a) Robert Brown
b) Robert Hooke
c) Charles Darwin
d) Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Correct Answer: b) Robert Hooke
2. Which part of the cell is called the powerhouse?
a) Nucleus
b) Mitochondria
c) Ribosome
d) Cytoplasm
Correct Answer: b) Mitochondria
3. Green colour in plants is due to the presence of:
a) Chromoplasts
b) Leucoplasts
c) Chloroplasts
d) Cytoplasm
Correct Answer: c) Chloroplasts
4. The jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus is called:
a) Cell wall
b) Plastid
c) Cytoplasm
d) Vacuole
Correct Answer: c) Cytoplasm
5. Cell walls are found in:
a) Animal cells only
b) Plant cells only
c) Both plant and animal cells
d) None of these
Correct Answer: b) Plant cells only (Note: Also found in bacteria/fungi, but in the context of plant vs animal, this is correct).
6. The control centre of the cell is the:
a) Nucleus
b) Cytoplasm
c) Cell membrane
d) Vacuole
Correct Answer: a) Nucleus
7. Chromosomes are found inside the:
a) Nucleolus
b) Nucleus
c) Cytoplasm
d) Vacuole
Correct Answer: b) Nucleus
8. Which of the following cells can change its shape?
a) White blood cell (WBC)
b) Red blood cell (RBC)
c) Nerve cell
d) Muscle cell
Correct Answer: a) White blood cell (WBC) (Amoeba is another example).
Class 8 Science Chapter 15
Class 8 Science Chapter 13
#Cell Structure and Functions Class 8
